Figure 2.
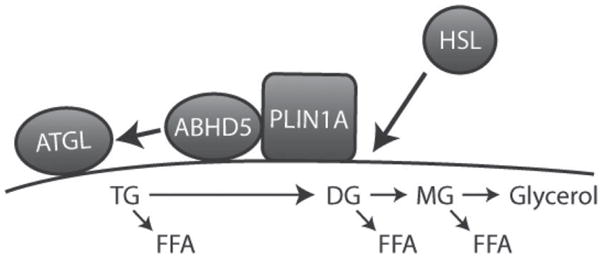
Protein trafficking during initiation of lipolysis. Under basal conditions, perilipin1A (PLIN1A) and α/β hydrolase domain-containing 5 (ABHD5) form a complex on the surface of lipid droplets (LD). Hormone-sensitive lipase (HSL) is mainly cytosolic, whereas adipose triglyceride lipase (ATGL) is localized to LD, including those containing perilipin (PLIN). Stimulation by protein kinase A (PKA) activation leads to trafficking of HSL and ABHD5 (arrows). Phosphorylation of PLIN1A induces a conformational change that decreases its proximity to ABHD5, which allows ABHD5 to activate ATGL. Because ATGL acts exclusively on triglyceride (TG), it is likely that ATGL initiates generation of FFA. Phosphorylation of HSL promotes its translocation and tight association with PLIN1. A major component of HSL activity likely depends on generation of diglyceride (DG) substrate from the action of ATGL, whereas monoglyceride lipase (MG) acts to liberate glycerol and the final FFA. Not illustrated are potential effects of PLIN phosphorylation on the biophysical properties of the LD surface and the effects of sustained activity on LD fragmentation and movement.
