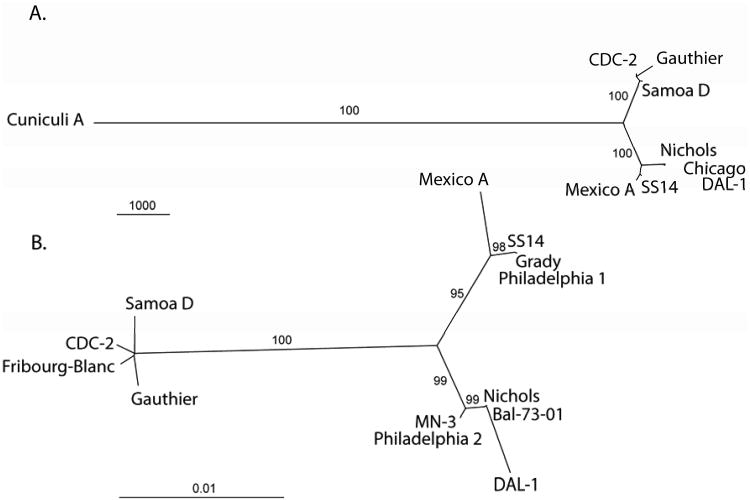
Fig. 1.
A. An unrooted tree constructed from whole genome sequence alignments using the maximum parsimony method. The bar scale corresponds to 1000 nt changes. Bootstrap values based on 1,000 replications are shown next to branches. The tree is very similar to that obtained following analysis of binary restriction target site data (Mikalová et al., 2010).
B. An unrooted tree constructed from concatenated nucleotide sequences of TP0136, TP0326, TP0488, and TP0548 genes using the maximum likelihood method. The length of sequenced regions ranged from 8342 to 8412 nucleotides. The bar scale corresponds to 0.01 nt changes per site. Bootstrap values based on 1,000 replications are shown next to branches. The TPA strains cluster into two separate groups, one containing the Nichols and the second the SS14 strain. In addition to strains listed in the Table 1, TPA strains Grady, Philadelphia 1, Philadelphia 2, MN-3, and Bal-73-01 are shown.