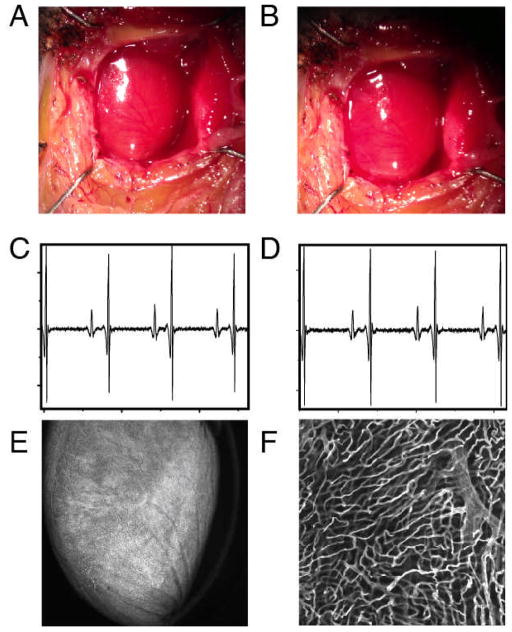
Fig. 5.
White light image of the heart before (A) and after (B) application of the stabilization holder. After removal of the stabilizer no damage is evident from the images. ECG signals acquired at different times before the intravital imaging session (C) and after the stabilizer has been positioned on the heart (D). No noticeable differences are present in the ECG signals, indicating normal electrical heart activity during the imaging session. (E,F) In order to demonstrate that the stabilizer did not alter the capillary structures, the mouse was injected intravenously with 50 μL of a 10nM solution of Griffonia simplicifolia-I lectin (Ex 550nm, Em 575nm), which binds specifically to the mouse endothelial cells staining the capillaries. After removal of the stabilizer the mouse was euthanized and the heart immediately imaged. No damage was present in the microvascular network on the surface of the heart at both the macroscopic (E) and microscopic (F) level. (F) was acquired in confocal mode at a depth of ca. 50 microns in the point of contact between the stabilizer and the heart.