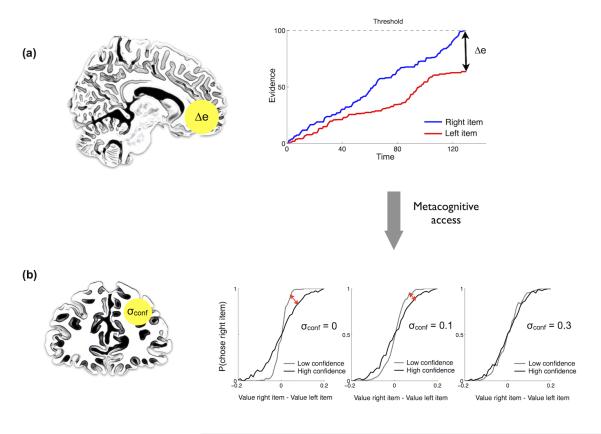
Figure 6. Schematic of network relating confidence to subjective report.
Summary of the relationship between our computational model and neuroimaging analyses. (a) Confidence in the decision (Δe) emerges from the value comparison process instantiated in vmPFC. (b) In order to reach metacognitive awareness (and be reported by the participant) this information is transferred to rRLPFC. An additional parameter (σconf) governs the noise in the read-out of Δe (i.e. decision confidence). If σconf is zero the information about confidence (Δe) is uncorrupted, resulting in a pronounced shift in the choice accuracy between high confidence and low confidence trials (red arrow). As the level of metacognitive noise increases (more positive values of σconf ) the shift between the two curves (low and high confidence) diminishes. Differences in σconf account for the inter-subject variability in metacognitive reportability we observed behaviorally.