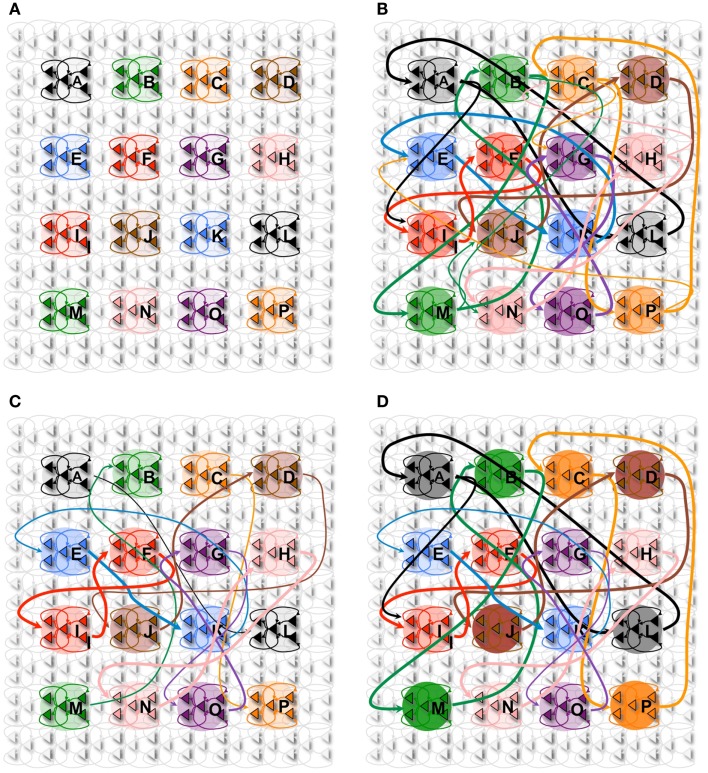
Figure 5.
Declarative memory task. (A) The network with 16 neuronal groups before it is trained. (B) The network with 16 neuronal groups is trained to learn 8 pair associations. However, other connections are also potentiated due to spontaneous activations as well as mistake sequences encountered during learning. Neuronal group color saturation indicates its frequency of activation in wake. (C) After sleep, activation protects the learned pairs significantly more than the other connections between groups. Neuronal group color saturation indicates its frequency of activation in sleep. (D) After training in wake (B), half of the associative pairs are cued during sleep (Pairs A-L, B-M, C-P, D-J). The neuronal group color saturation indicates its frequency of activation in sleep, which is greater for the cued pairs. As a result, cued pairs are significantly protected and subsequently have a higher recall rate and S/N.