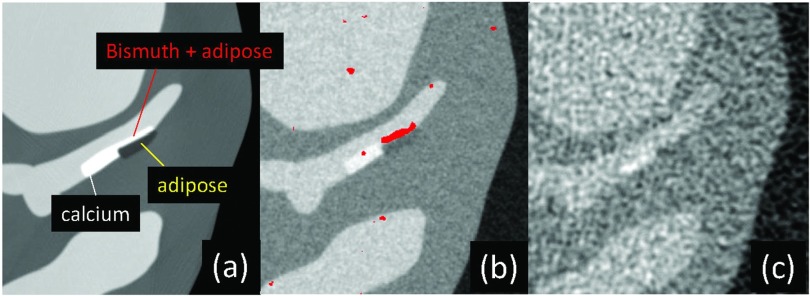
Figure 12.
(a) A computer simulated XCAT phantom image with bismuth at the surface of fatty atherosclerosis in a coronary artery (a). (b) and (c) Reconstructed images of the phantom scanned at the equivalent dose using a PCD-CT (b) and an EID-CT (c). Densities of bismuth are shown in red in (b). The PCD image has a better contrast-to-noise ratio and appears sharper than the EID image. This is also an example of K-edge, molecular, and simultaneous multiagent imaging. Reprinted with a modification from J. Cammin, et al., “Spectral response compensation for photon counting clinical x-ray CT and application to coronary vulnerable plaque detection,” Proceedings of the Second International Meeting on Image Formation in X-Ray Computed Tomography, edited by F. Noo (Salt Lake City, UT, 2012) pp. 186–189 (Ref. 113).