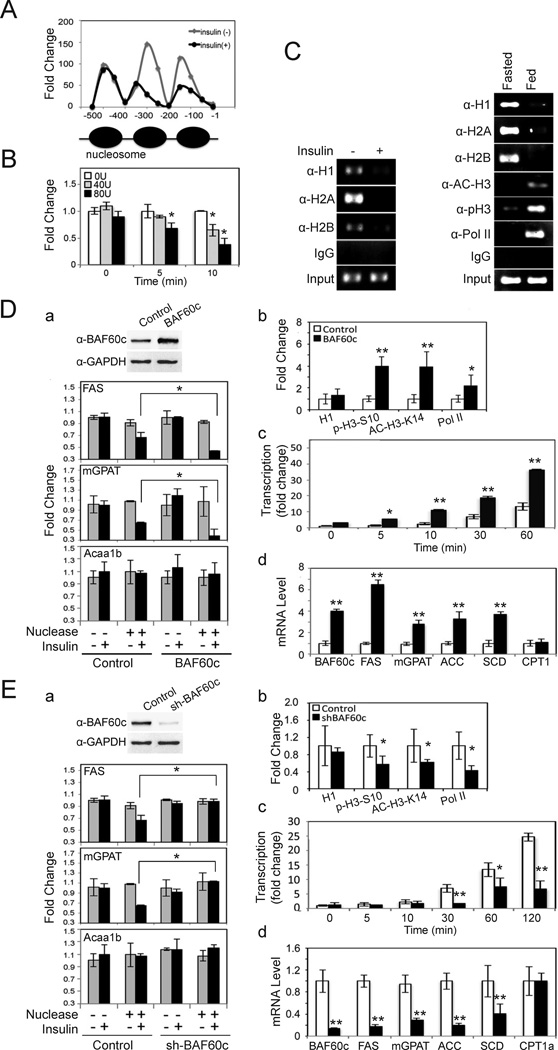
Figure 6. BAF60c enhances chromatin modification of lipogenic genes in response to insulin.
(A) Nuclear extracts from HepG2 cells treated with insulin for 10 min were subjected to MNase assay using 80U/ml. qPCR using primers spanning 500 bp of the FAS promoter region. (B) MNase assay in HepG2 cells treated with insulin. Fold change over non-MNase treated cells. Means ± SEM. *p<0.05. (C) ChIP assay in HepG2 cells (left) and in mouse livers (right). (D) a; BAF60c protein levels in HepG2 cells infected with control or BAF60c adenovirus (top). Infected cells treated with insulin for 10 min for MNase assay (bottom). b; ChIP for the FAS promoter region in HepG2 cells after 10 min of insulin treatment using anti-H1, anti-p-H3-S10, anti-Ac-H3-K14, and anti-Pol II antibodies. qPCR for the FAS promoter. c; Nuclear run-on assay for FAS transcription in cells infected with BAF60c after insulin treatment. RT-qPCR for FAS run-on assay. d; RT-qPCR for lipogenic gene expression in cells overexpressing BAF60c. Means ± SEM. *p<0.05, **p<0.01. (E) a; BAF60c protein levels in shBAF60c adenovirus infected cells (top). MNase assays by qPCR (bottom). b; ChIP for FAS promoter in HepG2 cells after BAF60c knockdown. c; Run-on assay using RT-qPCR for FAS transcription. d; Lipogenic gene expression by RT-qPCR in BAF60c knockdown cells. Means ± SEM. *p<0.05, **p<0.01.