Figure 5.
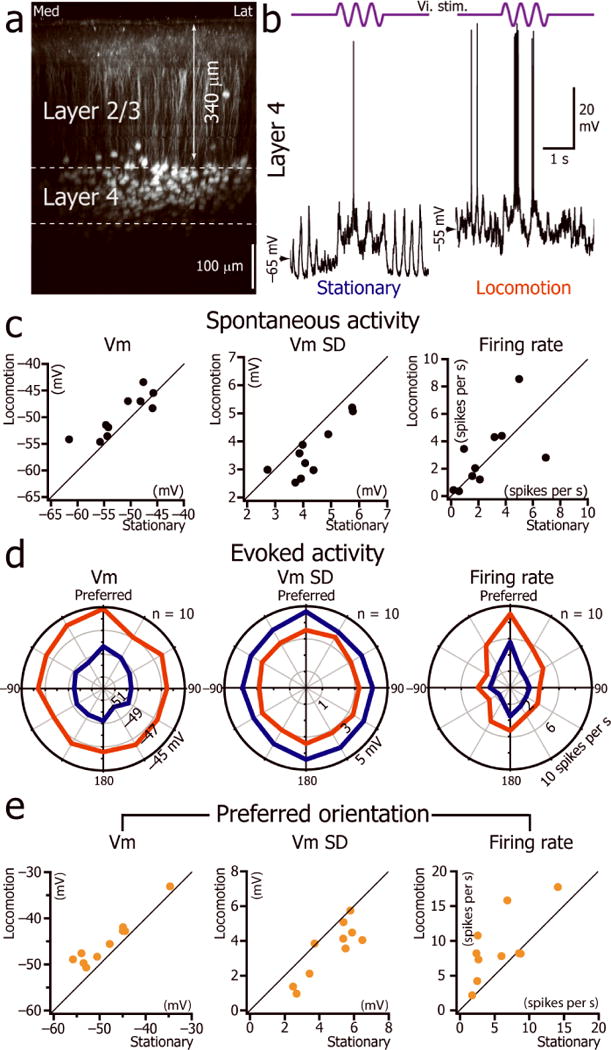
L4 neuron signal-to-noise ratio increases during locomotion. (a) Coronal view of V1 in a SCNN1a-Cre × Ai9 mouse expressing tdTomato in L4. (b) Current-clamp whole cell recordings from a V1 L4 neuron during the presentation of a 2Hz drifting grating of preferred orientation (top trace) when the animal was immobile (left) or during locomotion (right). (c) Plots of the spontaneous Vm, Vm SD and firing rate of L4 neurons during immobility versus locomotion (n= 10neurons from 10 mice). (d) L4 population orientation tuning curve for Vm, the Vm SD and firing rate during immobility and locomotion (n=10 neurons from 10 mice). (e) Plot of mean Vm, Vm SD and mean firing rate during immobility versus locomotion for the preferred orientation.
