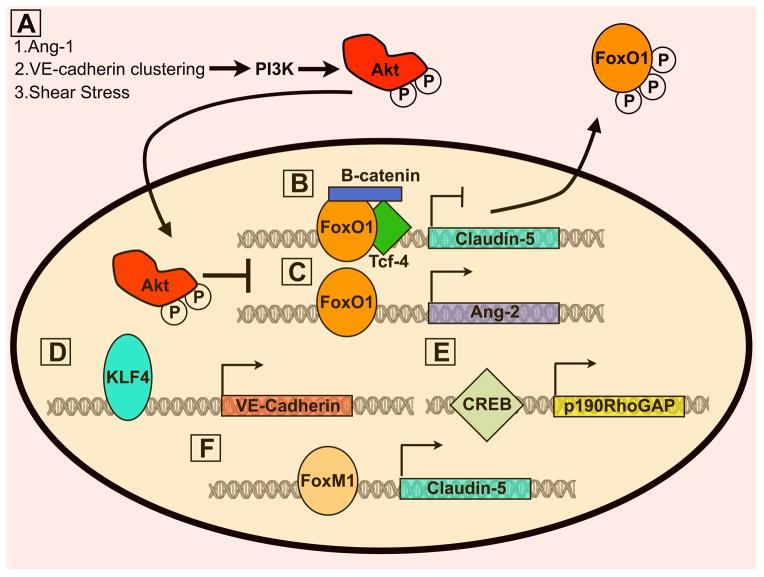
Figure 5. Transcriptional regulation of vascular permeability.
A) Akt phosphorylation by several stimuli results in FoxO1 phosphorylation and nuclear translocation. Subsequently, FoxO1 target genes including claudin-5 (B) and Ang-2(C) are expressed and repressed, respectively. Claudin-5 inhibition by FoxO1 requires complex formation between β-catenin and Tcf. Therefore, VE-cadherin/β-catenin complex formation is important for claudin-5 expression as it prevent β-catenin translocation to the nucleus. D) KLF4 stabilises the barrier by enhancing expression of VE-cadherin. E) CREB upregulates p190RhoGAP, which is important for inhibiting RhoA activation at adherens junctions. F) Both estrogen receptor (not depicted) and FoxM1 increase claudin-5 expression, thus promoting barrier stability.