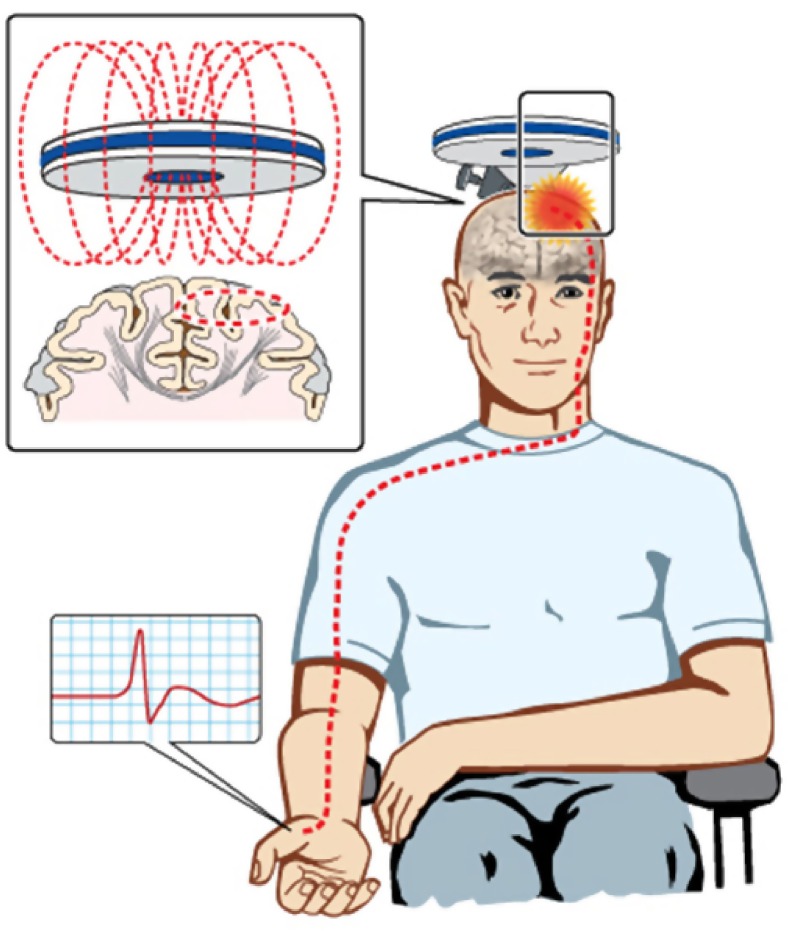
Figure 1.
Transcranial magnetic stimulation excites a network of neurons in the underlying motor cortex with motor evoked potentials recorded over the contralateral abductor pollicis brevis muscle. The motor cortex is preferentially stimulated when the current flows in a posterior–anterior direction within the motor cortex.