Figure 3.
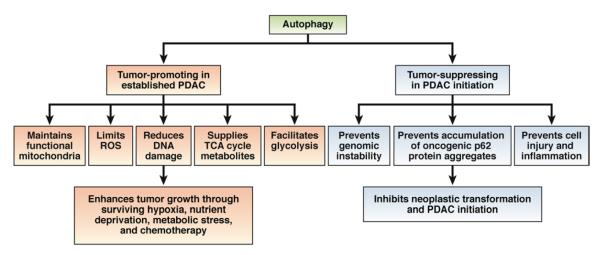
Dual role of autophagy in PDAC development. PDAC cells require efficient autophagy to survive hypoxia, nutrient deprivation, metabolic stress, and exposure to chemotherapeutic agents. Basal autophagy therefore promotes growth of PDACs by maintaining functional mitochondria, reducing ROS and DNA damage, supplying tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle metabolites, and facilitating glycolysis. In contrast, autophagy suppresses PDAC initiation: it limits ROS production, genomic damage, cell injury, and inflammation; and eliminates oncogenic aggregates of p62, to prevent transformation of epithelial cells.
