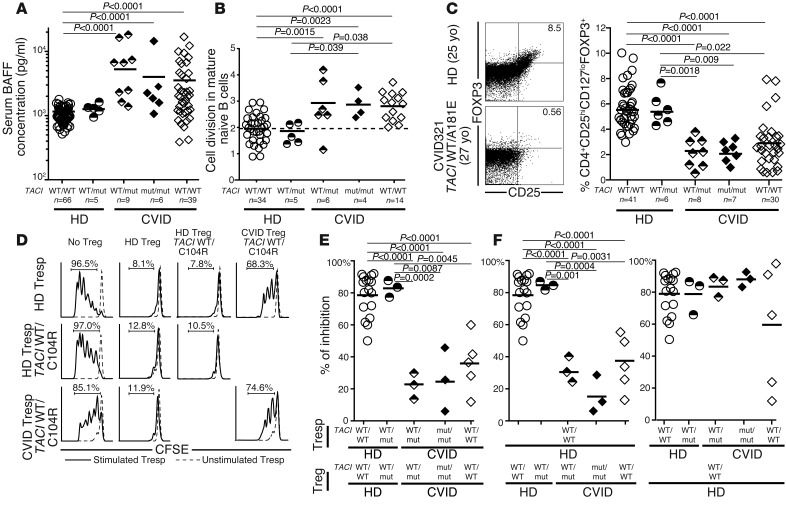
Figure 5. Increased plasma BAFF concentrations, homeostatic naive B cell proliferation, and an impaired Treg compartment are features common to CVID patients with and without TACI mutations.
TACI mutations did not affect plasma BAFF concentrations (pg/ml) measured by ELISA (A) or mature naive B cell expansion detected by KREC analysis (B). Both were greater in CVID patients compared with healthy controls. (C–F) CVID status, but not TACI mutations, affected Treg frequency and function. (C) Dot plots represent CD4+ gated CD25hiFOXP3+ T cells of a healthy donor control and an age-matched CVID patient with one TACI mutation. Scatter plots reveal that decreased CD4+CD25hiCD127loFOXP3+ Treg frequency only correlated with CVID. yo, year-old. (D) Representative histograms of Treg-mediated suppression of autologous and heterologous CFSE-labeled Tresp cells on day 4.5 from a CVID patient and a healthy relative both carrying a TACI mutation were compared with a healthy control. Dashed lines display nonstimulated Tresp cells. The autologous and heterologous suppressive activities of Tregs from healthy donor controls, healthy carriers with a single TACI mutation, CVID patients with one or two mutated TACI alleles, as well as CVID patients without TACI mutations are summarized in E and F, respectively. Statistical significance is indicated by an unpaired Student’s t test.