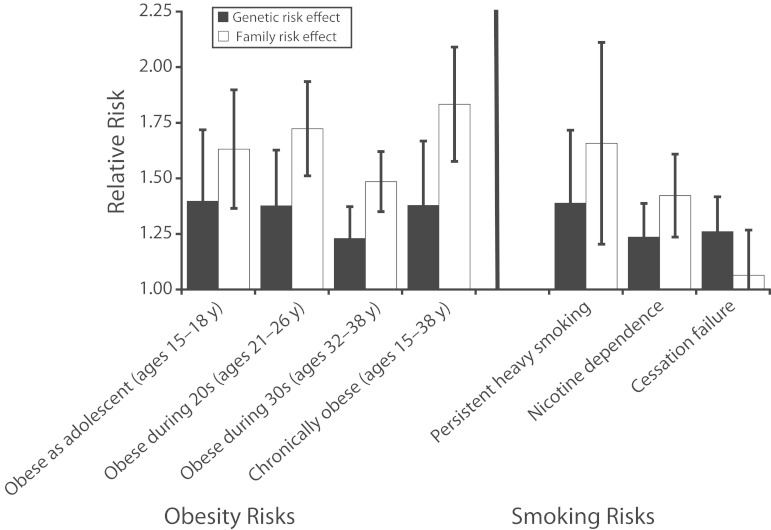
FIGURE 1—
Risks for obesity and smoking associated with genetic and family history-based risk scores: Dunedin Multidisciplinary Health and Development Study, 1972–2013.
Note. Effect sizes are shown as increments in the relative risk of the outcome associated with a 1 SD increase in the risk score. The obesity family history risk score was based on parental body mass index. The smoking family history risk score was based on the smoking behavior of cohort members’ parents, siblings, and grandparents. Error bars reflect 95% confidence intervals. Chronic obesity was defined as being obese at ≥ 3 of the 6 assessments between ages 15 and 38 years. Persistent heavy smoking was defined as smoking 20 or more cigarettes/day at ≥ 3 of the 6 assessments between ages 15 and 38 years. Cessation failure was defined for cohort members who smoked daily during their 30s as being unable to quit for at least 1 year through the time of the age 38-year assessment.