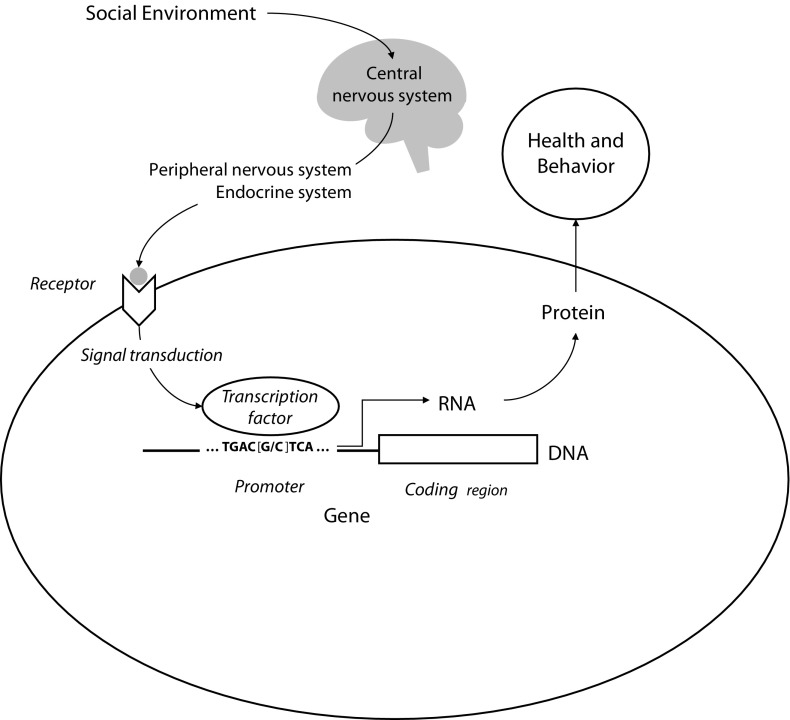
FIGURE 1—
Social signal transduction.
Note. Socioenvironmental conditions regulate human gene expression by activating central nervous system processes that subsequently influence hormone and neurotransmitter activity in the periphery of the body. Peripheral signaling molecules interact with cellular receptors to activate transcription factors, which bind to characteristic DNA motifs in gene promoters to initiate (or repress) gene expression. Only genes that are transcribed into RNA actually have an impact on health and behavioral phenotypes. Individual differences in promoter DNA sequences (e.g., the [G/C] polymorphism shown here) can affect the binding of transcription factors and thereby influence genomic sensitivity to socioenvironmental conditions.