Figure 4.
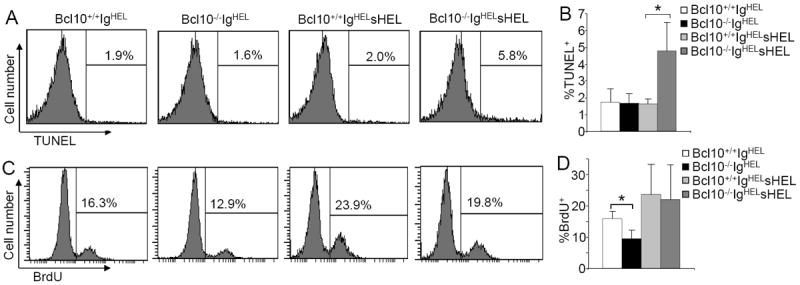
Increased apoptosis and normal proliferation of anergic B cells in Bcl10-deficient IgHELsHEL mice. A, TUNEL labeling of splenic B cells. Splenocytes from Bcl10+/+IgHEL, Bcl10-/-IgHEL, Bcl10+/+IgHELsHEL and Bcl10-/-IgHELsHEL transgenic mice were stained with anti-B220 antibodies. Then, the degree of TUNEL labeling in B220+ cells were determined by FACS analysis. Percentages indicate TUNEL+ cells in the gated B220+ cells. B, Statistical analysis of the percentages of TUNEL+ cells from panel A. C, BrdU incorporation in splenic B cells. BrdU was injected into Bcl10+/+IgHEL, Bcl10-/-IgHEL, Bcl10+/+ IgHELsHEL and Bcl10-/-IgHELsHEL transgenic mice. Splenocytes from the mice were stained with anti-B220 antibodies, followed by BrdU staining. Percentages indicate BrdU+ cells in the gated B220+ cells. D, Statistical analysis of the percentages of BrdU+ cells from panel C. Data shown are obtained from at least 5 (A and B) or 7 (C and D) mice in each group. Error bars show ± SD. *, P < 0.01.
