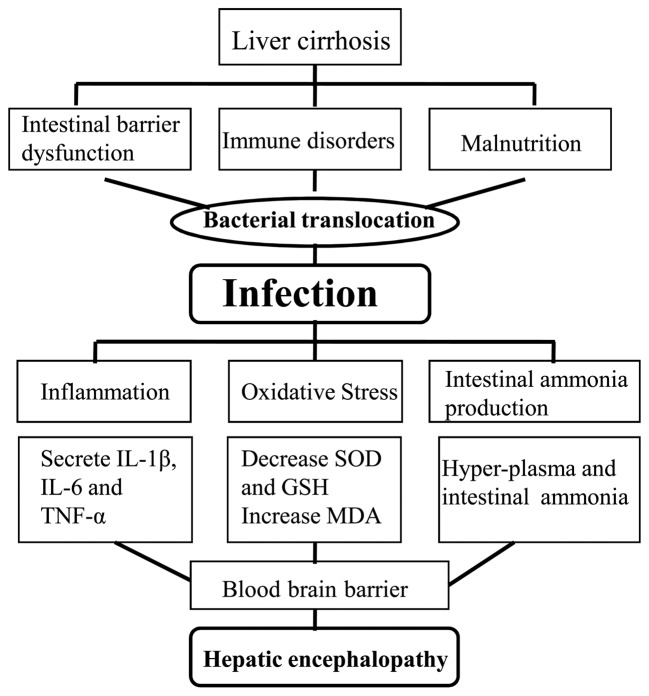
Figure 3.
Infection-induced hepatic encephalopathy in liver cirrhosis. Patients with liver cirrhosis develop intestinal barrier dysfunction, immune disorders and malnutrition due to portal hypertension. Bacteria then invade the body via the respiratory, intestinal and urinary tracts and result in various infections. Infection may activate inflammatory reaction and oxidative stress, and cause the secretion of several cytokines, including IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF-α. Reduced cerebral SOD levels and increased production of intestinal ammonia is observed in patients with HE. These inflammatory mediators selectively cross the blood-brain barrier and lead to hepatic encephalopathy (brain injury, edema). IL-1β, interleukin-1β; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α; SOD, superoxide dismutase; GSH, glutathione; MDA, malondialdehyde; HE, hepatic encephalopathy.