Figure 4.
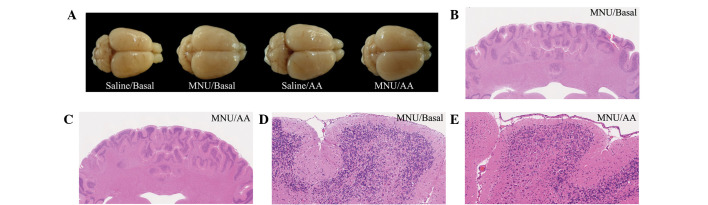
Macroscopic and histopathological brain lesions in rats treated with 35 mg/kg N-methyl-N-nitrosourea (MNU) or saline only at birth. (A) Dorsal views of brains from 28-day-old rats. Left end, saline-treated control rat fed the basal diet (Saline/Basal); second from the left, MNU-treated rat fed the basal diet (MNU/Basal); right middle, saline-treated control rat fed the arachidonic acid (AA)-rich diet (Saline/AA); far right, MNU-treated rat fed the AA-rich diet (MNU/AA). Note the reduction in the cerebellar cortex in the specimens from MNU-treated animals, the disappearance of the cerebellar vermis tubercle and the appearance of quadrigeminal bodies. (B-E) Histopathological lesions of the cerebellum in the MNU/Basal (B and D) and MNU/AA (C and E) rats. Hypoplasia of the cerebellar cortex in MNU-treated rats fed each diet (AA or basal) [B and C; hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining; magnification ×13]. Disorganization of cerebellar cortex, characterized by the disarrangement of cortical layers and loss and/or disturbance of the molecular, Purkinje and granular cell layers (D and E; HE staining; magnification, ×100).
