Figure 4. Morphology and gene expression levels of RPCs under differentiation conditions.
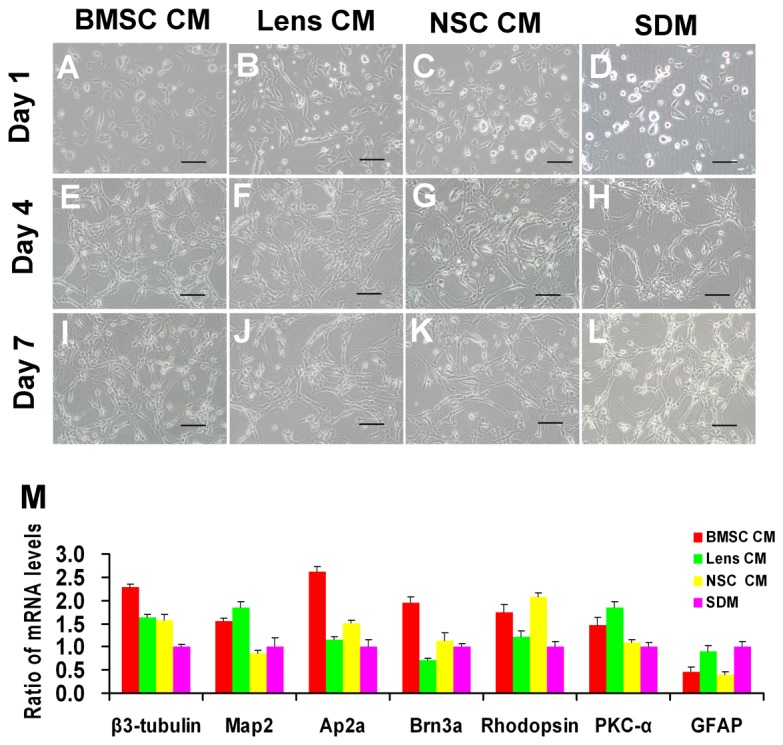
One day after the cells were cultured in the differentiation conditions, the cells in the differentiation medium without CM only occasionally extended short processes (D), whereas most of the cells extended short processes in the CM-treated cultures (A, B, C). Under differentiation conditions, RPCs treated with BMSC CM (A, E, I), lens CM (B, F, J), NSC CM (C, G, K) and SDM (D, H, L) typically exhibited increasing neurite-like cellular processes and formed a network among the cells with time. However, the cellular processes of RPC cultures treated with CM, especially with BMSC CM, were longer and appeared more numerous than in the control cultures (without CM treatment). In the qPCR analysis (M), a notable up-regulation in the expression of β3-tubulin, activator protein 2 alpha (Ap2α, an amacrine cell marker) and Brn3a (a ganglion cell marker) was detected in the BMSC CM-treated RPC cultures. The levels of the neuronal markers MAP2 and PKC-α (a marker for bipolar cells) were significantly higher in the BMSC CM- and lens CM-treated RPC cultures compared with the control. The expression levels of rhodopsin (a photoreceptor marker) were higher in RPC cultures treated with BMSC CM or NSC CM. In addition, low expression levels of the glial marker GFAP were found in the RPC cultures treated with CM. Scale bars: 100 µm.
