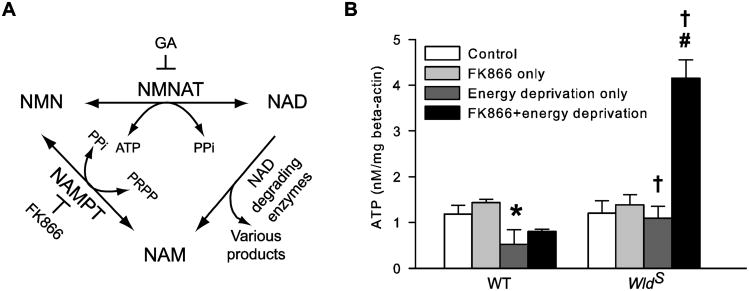
Figure 7.
Inhibiting NMNAT-catalyzed NAD synthesis by FK866 alleviates axon ATP loss caused by energy deprivation. A, Schematic illustration of the salvage pathway of NAD resynthesis from NAM. The salvage pathway utilizes NAM produced by such constitutive NAD degrading enzymes as poly(ADP-ribose) polymerases, ADP-ribose transferasses, cADP-ribose synthases, and sirtuins to resynthesize NAD at the expense of ATP. The pathway consists of two consecutive reactions catalyzed by NAMPT and NMNAT, respectively. FK866 specifically blocks the production of NMN by NAMPT. GA is a putative inhibitor of NMNAT. B, FK866 reduces axon ATP loss caused by energy deprivation. WT and WldS [ATP]axon were determined immediately after the following treatments: sham wash and vehicle control (control), FK866 for 1h (FK866 only), energy deprivation for 30 min (energy deprivation only), and FK866 for 1h followed by 30 min energy deprivation in the absence of FK866 (FK866+energy deprivation). The data were acquired from an average of eight samples per group. *, P < 0.05 compared to any other WT group; #, P = <0.001 compared to any other WldS group; †, P < 0.05 compared to the corresponding WT group.