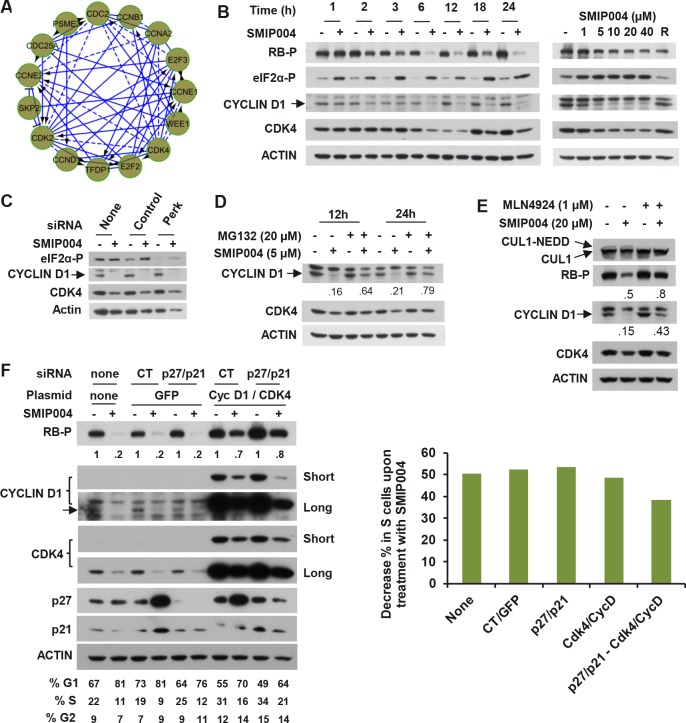
Figure 3. Effect of SMIP004 on cell cycle pathways.
(A) RB subnetwork components downregulated by SMIP004 as revealed by Reactome network analysis (B) Kinetics and dose response of SMIP004 effects on RB pathway components as revealed by immunoblotting. LNCaP-S14 cells were treated with 40 μM SMIP004 for the indicated times (left panel) or were treated for 24 h with the indicated doses of the compound (right panel). (C) LNCaP-S14 cells were transfected with siRNA for PERK, followed by treatment with DMSO or SMIP004 (40 μM). The levels of cyclin D1, CDK4 and eIF2α-P were determined by immunoblotting. (D) Cells were pre-incubated with MG132 for 1h followed by treatment with SMIP004 for the indicated times. Cyclin D1 and CDK4 levels were analyzed by immunoblotting. (E) Cells were pre-treated with the neddylation inhibitor MLN4924 (1 μM) for 1h followed by treatment with SMIP004 (20 μM) for 6h. Levels of cyclin D1, CDK4, RB-P and cullin 1 (neddylated and unneddylated forms) were evaluated by immunoblotting. (F) LNCaP-S14 cells were transfected with p27 and p21 siRNAs for 24 h followed by transient transfection with cyclin D1 and CDK4 expression plasmids for another 24 h. Cells were then incubated for an additional 24 h in the presence or absence of SMIP004 (40 μM). Cells were collected for flow cytometry and immunoblotting analysis. Quantifications of phospho-RB levels are relative to the loading control actin. Short and long exposures are shown for cyclin D1 and CDK4 blots. The right panel shows the effects of the various genes on SMIP004-induced decrease in the S phase population.