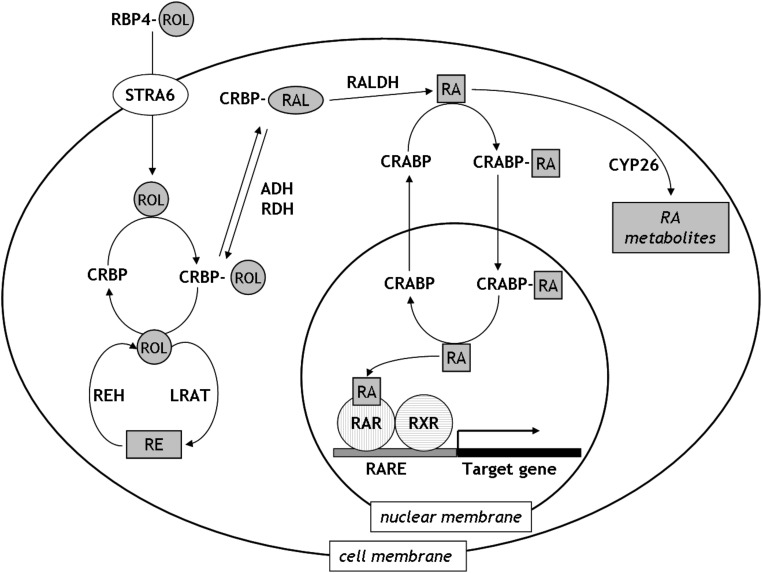
FIG. 1.
Retinoid metabolism. In the circulation, ROL is bound to RBP4. It can be taken up by cells by facilitated transport via STRA6 receptors. Within the cell, ROL is carried by CRBPs and can be stored in the form of REs or converted to RA in a two step process. RA is transported to the nucleus upon binding to CRABPs and acts through the activation of RA receptor heterodimers. Excess RA can be metabolized by the CYP26 enzymes. RE, retinyl ester; RAL, retinaldehyde; ROL, retinol; RA, retinoic acid; RBP4, retinol binding protein 4; STRA6, receptor for the ROL/RBP4 complex; CRBP, cellular ROL binding protein; CRABP, cellular RA binding protein; ADH, alcohol dehydrogenase; RDH, ROL dehydrogenase; RALDH, retinaldehyde dehydrogenase; REH, retinyl ester hydrolase; LRAT, lecithin ROL acyltransferase; RAR, RA receptor; RXR, retinoid X receptor; CYP26, a family of cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzymes.