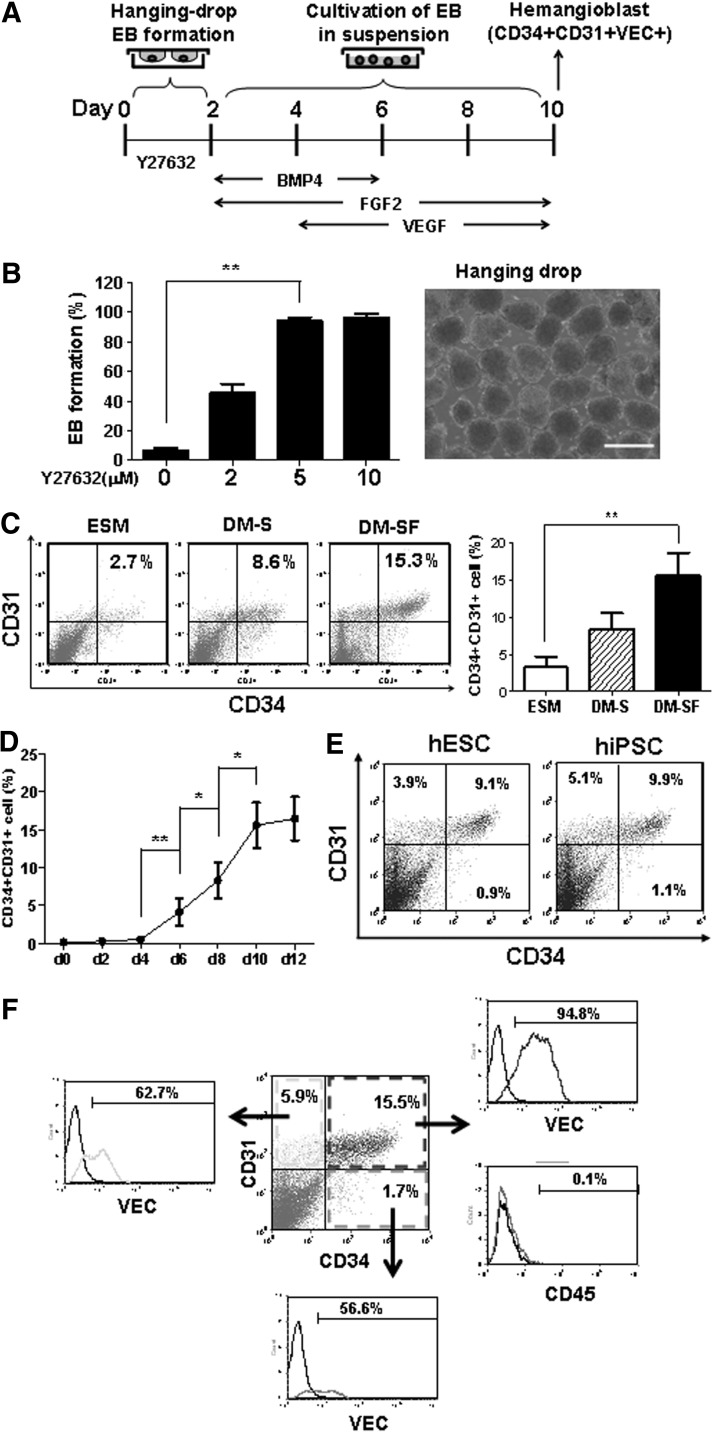
FIG. 1.
Differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells (hPSCs) in embryoid bodies (EBs). (A) Schematic diagram of hPSC differentiation. EBs were initialized in hanging drops. After 2 days, EBs were collected into ultralow attachment dishes with growth factors as indicated. (B) Rho-dependent protein kinase (ROCK) inhibitor, Y27632, enhanced EB formation in hanging drops from day 0 to 2. The percentages of EB formation in hanging drops were counted after 2 days in the presence of different Y27632 concentrations (left panel). A representative morphology of EBs at day 2 was shown (right panel). Scale bar=500 μm. (C) Media for hPSC differentiation from day 2 to 10, including the ESC culture medium (ESM), serum-containing differentiation medium (DM-S), and serum-free differentiation medium (DM-SF). Flow cytometry analyses were performed at day 10. (D) The kinetics of hPSC differentiation to CD34+CD31+ cells. Flow cytometry analyses were performed every 2 days in triplicate experiments. (E) Differentiation of human embryonic stem cells (hESCs) and human induced-pluripotent stem cells (hiPSCs) to CD34+CD31+ cells. Flow cytometry analyses were performed at day 10. (F) CD34+CD31+VEC+ population from hPSC differentiation. Flow cytometry analyses were performed at day 10 of hPSC differentiation. Data are represented as mean±SD from three independent experiments. *P<0.05, **P<0.01.