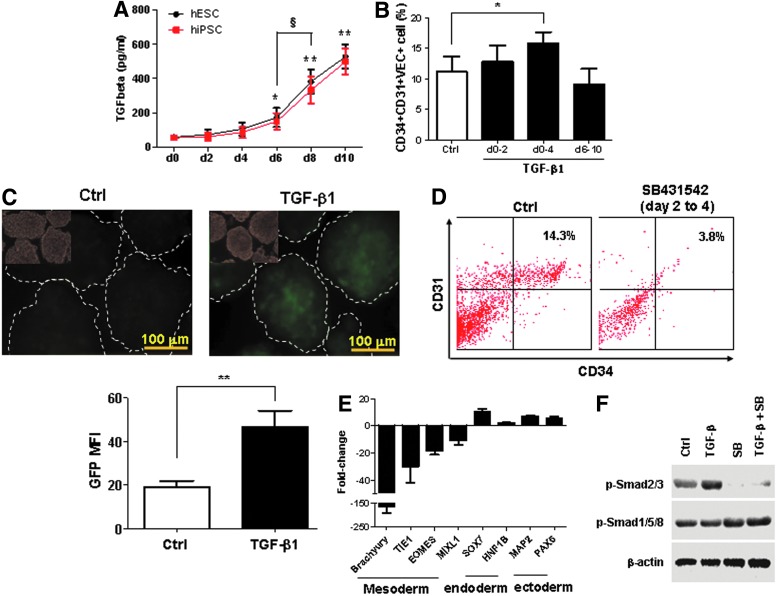
FIG. 5.
Positive effect of transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) signaling on early mesodermal development. (A) The kinetics of TGF-β secretion during EB differentiation. The cultured media were collected for ELISA assay every 2 days before changing to fresh media. The TGF-β concentration in cultured media with hESCs (H1) and hiPSCs (HSFa-YK26) were measured by the Quantikine ELISA kit. (B) Promoting effect of TGF-β1 on CD34+CD31+VEC+ cells during early mesoderm development. TGF-β1 (2 ng/mL) was added to EB differentiation at different time points. Flow cytometry analyses were performed at day 10 of EB differentiation. (C) EBs were generated from hiPSC BC1-Brachyury-GFP, in which the GFP expression is driven by the Brachyury promoter, in the medium with or without 2 ng/mL TGF-β1 from day 0 to 2. The morphology and GFP expression were examined at day 5. The GFP mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of individual EBs was quantified according to histogram of green channel by Photoshop software. (D) Impaired development of CD34+CD31+ cells by inhibition of TGF-β signaling during early mesoderm development. TGF-β inhibitor, SB431542, (10 μM) was added to EB culture from day 2 to 4. Flow cytometry analyses were performed at day 10 of EB differentiation. (E) qPCR analyses of three germ layer gene expressions. EB differentiation was performed with or without SB431542 from day 2 to 4. EBs were collected at day 4 for gene expressions analyses of mesodermal, endodermal, and ectodermal markers. (F) Western blot analysis of phosphorylated Smad. EBs from hiPSCs at day 2 were incubated with 10 ng/mL TGF-β1 and/or 10 μM SB431542 for 30 min. The phosphorylated Smad2/3 (p-Smad2/3) and p-Smad1/5/8 were detected by specific antibodies against p-Smad2/3 or p-Smad1/5/8. β-Actin was used a control. Data are represented as mean±SD from three independent experiments. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, compared with the day 0 group or indicated group. §P<0.05, between two groups.