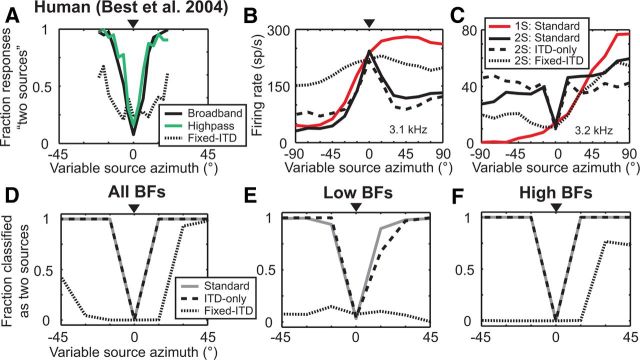
Figure 8.
Neural sensitivity to interaural decorrelation underlies the perception of source separation in front of a listener. A, Human perception of two sources as a function of separation between a fixed source (triangle) and a variable source for broadband noises (black solid line), high-pass noises (green line), and broadband noises in a fixed-ITD condition (dotted line). Data from Best et al., 2004. B, C, Azimuth tuning functions of two high-BF IC neurons to single sources (red line), and to a variable source in the presence of a concurrent fixed source (triangle) in the standard (black line), ITD-only (dashed line), and fixed-ITD (dotted line) conditions. BF of each neuron indicated in corner. D, Performance of the population-pattern decoder on distinguishing two concurrent, separated sources from single sources using all neurons (solid line; N = 43). Performance of the decoder using the same neurons when trained on data in the standard condition and tested on data either in the ITD-only (dashed line) or fixed-ITD (dotted line) conditions. E, F, Same as in D except the decoder used only neurons with low BFs (N = 11) or high BFs (N = 32), respectively.