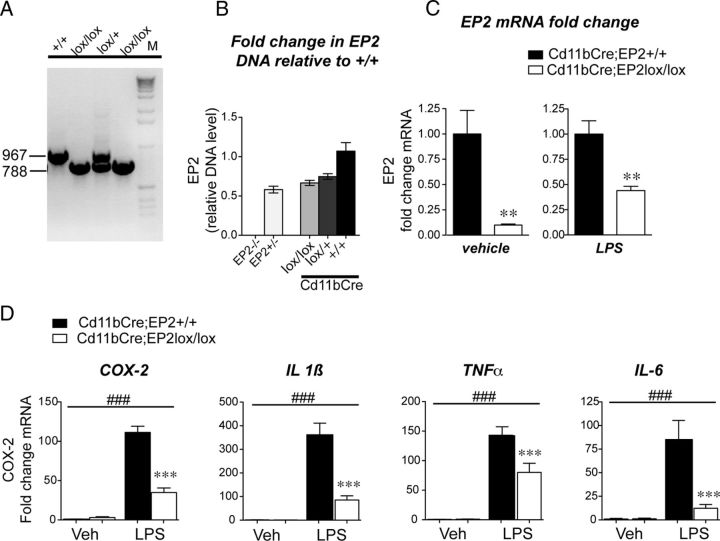
Figure 4.
Conditional deletion of the EP2 receptor in macrophages suppresses oxidative enzyme and cytokine gene expression. A, Genomic DNA PCR is shown for EP2+/+, EP2lox/+, and EP2lox/lox C57BL/6 mice. B, Quantitative genomic PCR was assayed for EP2+/+ wild-type, EP2+/−, EP2−/−, Cd11bCre;EP2lox/lox, Cd11bCre;EP2lox/+, and Cd11bCre;EP2+/+; values are relative to wild-type EP2+/+ control DNA. C, Peritoneal macrophages were isolated from adult Cd11bCre;EP2lox/lox and Cd11bCre;EP2+/+ mice and sorted using Cd11b antibody-conjugated magnetic beads before qPCR analysis. Basal levels of EP2 mRNA, assayed by qPCR, are reduced by 91% in Cd11bCre;EP2lox/lox compared with control macrophages (left; Cd11bCre;EP2lox/lox vs Cd11bCre;EP2+/+) and are reduced by 56% in LPS-stimulated Cd11bCre;EP2lox/lox macrophages (right; **p < 0.01; n = 5–6 per group). D, Conditional deletion of EP2 in macrophages reduces LPS-mediated increases in proinflammatory gene expression (two-way ANOVA for effect of LPS treatment is represented by ###p < 0. 001; Bonferroni's multiple-comparisons tests comparing mean of Cd11bCre;EP2+/+/LPS and Cd11bCre;EP2lox/lox/LPS were ***p < 0.001; n = 5–6 per group).