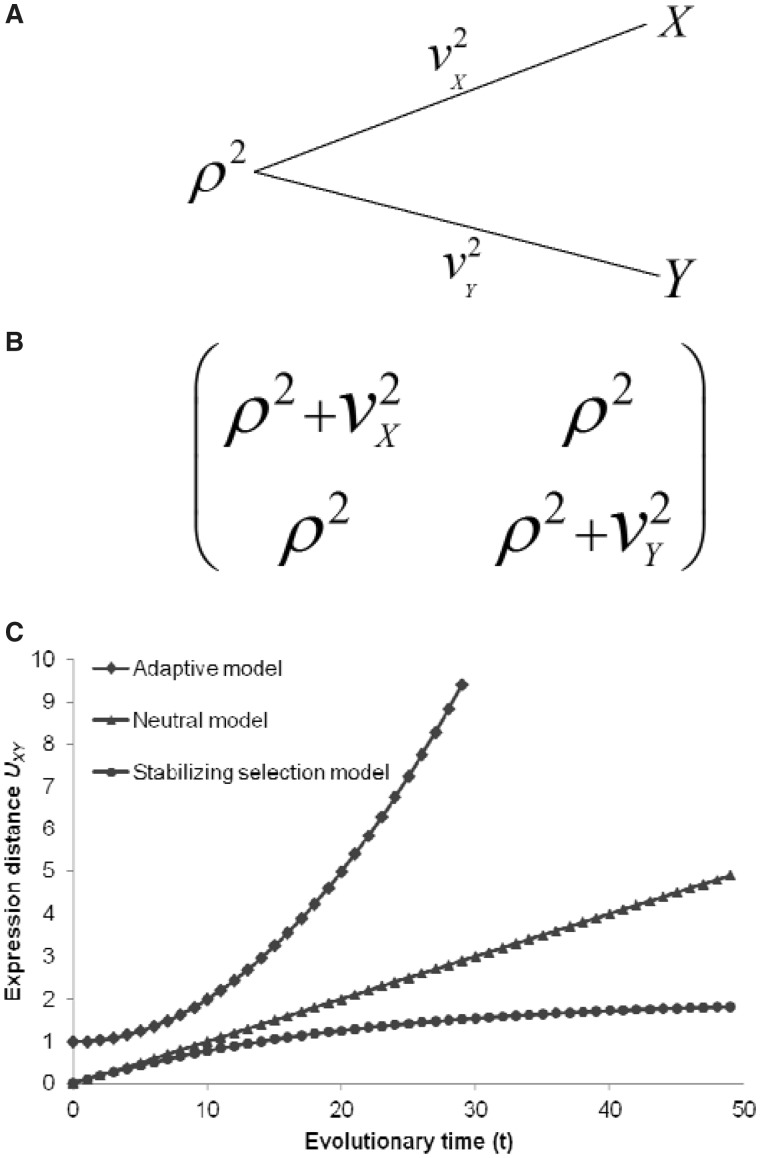
Fig. 1.—
Model of transcriptome evolution between two species. (A) A schematic illustration for a rooted two-gene tree: ρ2 refers to among-gene expression variability at the common ancestor of species X and Y; v2X and v2Y measure the among-gene expression variability in lineage X and Y since the split of common ancestor, respectively. (B) The variance–covariance matrix of genome expression between for current genomes X and Y. (C) The expression distance UXY plotted against the evolutionary time t. Expression divergence is an accelerated process under the adaptive model, a constant-rate process under the neutral model, and a decelerated process under the stabilizing model. In particular, when W→0, we have UXY →2σ2t, i.e., the stabilizing selection model is reduced to the neutral model; and when t→∞, UXY →1/W, i.e., the expression divergence approaches a saturated level.