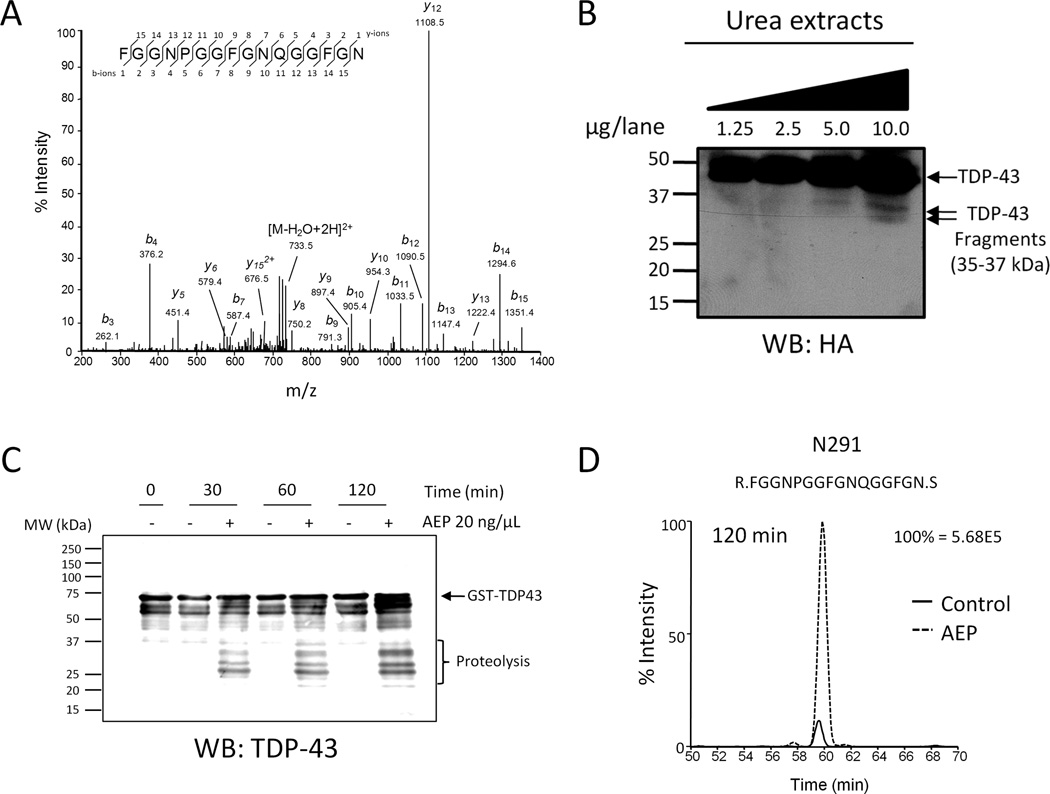
Figure 2. TDP-43 is an AEP substrate.
(A) Representative MS/MS spectra of TDP-43 partial tryptic peptides prematurely ending with C-terminal asparagine 291 (N291), that were identified in FTLD and HEK293 cell samples. (B) Western blot analysis of N-terminal TDP-43 cleavage products from cells expressing HA-TDP-43. HEK293 cells were transfected with plasmid expressing N-terminally tagged HA-TDP-43 and sarkosyl-insoluble fractions were prepared for parallel LC-MS/MS and western blot analyses. HA-immunoreactive TDP-43 cleavage products with predicted molecular weights of approximately 32 and 35 kDa were observed in urea extracts. (C) Asparaginyl endopeptidase (AEP) cleaves TDP-43 in vitro. Recombinant TDP-43 fused to GST was incubated with or without recombinant AEP for the indicated times at 37°C. Western blot revealed increased TDP-43 immunoreactivity ≤37 kDa over time in samples containing AEP. (D) Representative extracted ion chromatogram of N291 peptide from in vitro samples. TDP-43 semi-tryptic peptides prematurely ending with N291 were identified in samples with and without AEP at the 120 min time point, however the presence of AEP increased the abundance of these peptides approximately 10-fold. Data representative of three independent experiments.