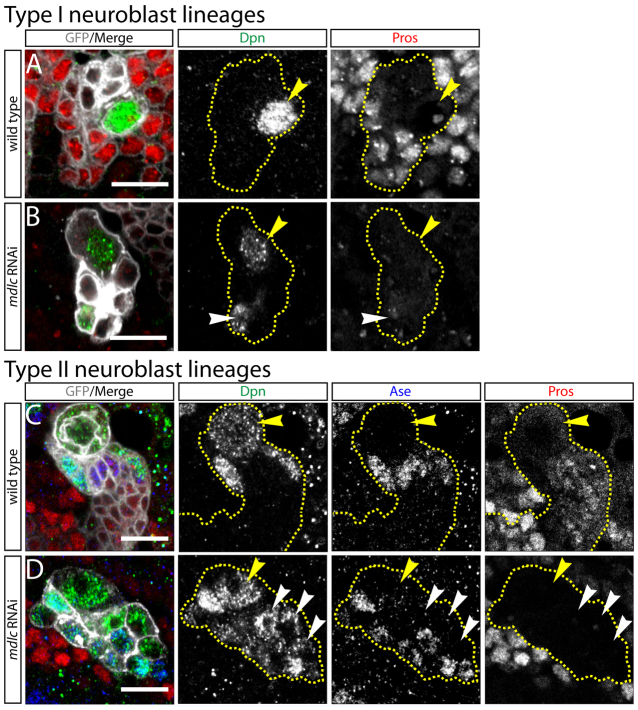
Fig. 1.
Knockdown of mdlc causes ectopic Dpn and loss of Pros in Drosophila larval neuroblast lineages. (A,B) Type I central brain neuroblast lineages. Yellow dashed lines indicate lineage boundaries; yellow arrowheads mark type I neuroblasts. (A) Wild-type (wt) lineages show a single large Dpn+ neuroblast and multiple smaller Pros+ neurons. (B) mdlc RNAi causes small ectopic Dpn+ cells (white arrowhead) as well as a strong loss of Pros in many neurons. (C,D) Type II central brain neuroblast lineages. Yellow dashed lines indicate lineage boundaries; yellow arrowheads mark type II neuroblasts. (C) Wt lineage showing Dpn+ type II neuroblast and Dpn+ mature INPs; Ase is absent from the type II neuroblast but present in mature INPs and GMCs. (D) mdlc RNAi lineage showing ectopic Dpn+ cells; some are Ase+ indicating an INP fate, whereas others are Ase- indicating reversion to a type II neuroblast-like fate. Pros staining is strongly reduced. Yellow arrowhead marks the presumptive type II neuroblast; white arrowheads indicate ectopic Dpn+ Ase- cells. Genotypes: (A) wor-Gal4 UAS-Dcr2; UAS-mCD8:GFP; (B) wor-Gal4 UAS-Dcr2/UAS-mdlc RNAi; UAS-mCD8:GFP; (C) UAS-Dcr2; wor-Gal4 ase-Gal80; UAS-mCD8:GFP; (D) UAS-Dcr2; wor-Gal4 ase-Gal80/UAS-mdlc RNAi; UAS-mCD8:GFP. Scale bars: 10 μm.