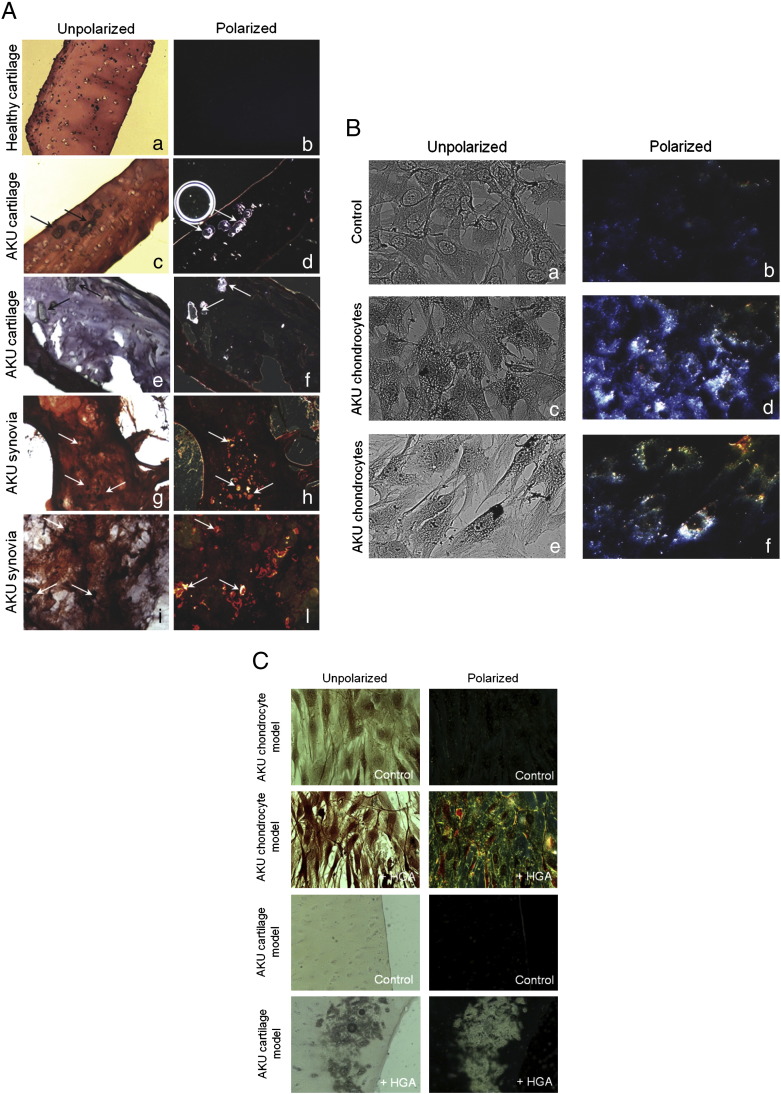
Fig. 1.
A) Congo Red stained AKU cartilage and synovia. A, B: Healthy cartilage; C, D: cartilage from Patient 4; E, F: cartilage from Patient 5. G, H: Synovia from Patient 4; I, L: synovia from Patient 5. Analogous results were obtained from specimens of other patients. M–P: Congo Red staining of HGA-treated human healthy cartilage sections. M: Control, untreated cartilage model; O, P: HGA-treated cartilage model. In O an ochronotic shard is well visible showing a remarkable birefringence in P. Arrows indicate ochronotic shards. Magnification 20 ×. Representative images from a triplicate set are shown. B) Congo Red stained AKU chondrocytes. Congo Red birefringence was observable in ex vivo AKU chondrocytes. A, B: Control, healthy human chondrocytes; C, D: chondrocytes from AKU Patient 1; E, F: chondrocytes from AKU Patient 7; Analogous results were obtained from specimens of other patients. Magnification 20 ×. Representative images from a triplicate set are shown. C) Congo Red stained cell and cartilage AKU models. Upper panels) Congo Red birefringence was observable in human primary cultured chondrocytes treated with 0.33 mM HGA. Control: untreated chondrocytes. Magnification 10 ×; Lower panels) Congo Red staining of 0.33 mM HGA-treated human healthy cartilage sections: an ochronotic shard is well visible showing a remarkable birefringence. Control: untreated cartilage. Magnification 20 ×. Representative images from a triplicate set are shown.