Fig. 9.
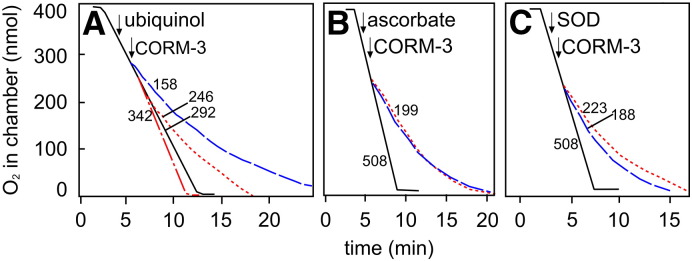
Antioxidants and superoxide dismutase (SOD) do not prevent CORM-3-dependent inhibition of respiration to the same extent as thiol compounds. Wild type E. coli membrane particles were added to the oxygen electrode in sonication buffer (2 ml) to a final concentration of approximately 60 μg/ml in (A) and 100 μg/ml in (B). The chamber was closed and respiration was initiated by the addition of 6.25 mM NADH. The first arrows in each panel indicate the addition of the antioxidant or enzyme: (A) ubiquinol (100 μM); (B) ascorbate (1 mM); (C) SOD (250 units) to the chamber, while the second arrows indicate the addition of CORM-3 (400 μΜ). The black solid lines show the uninhibited respiration rate, the blue dashed lines show oxygen consumption in the presence of CORM-3 and the red dotted lines show oxygen consumption in the presence of CORM-3 and the antioxidant (A and B) or SOD (C). In (A), the red dot dash line shows oxygen consumption in the presence of ubiquinol alone. Respiration rates (nmol min− 1 mg− 1 protein) 2 min following the addition of CO-RM are shown adjacent to each trace. Traces are representative of 2 biological replicates, each with 3 technical replicates.
