Fig. 4.
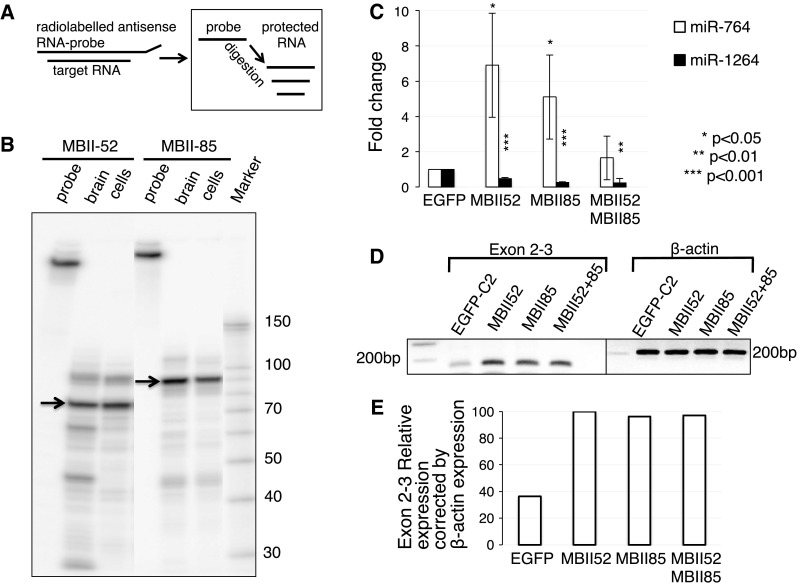
Influence of MBII-52 and MBII-85 overexpression on miRNAs. a Schematic illustration of the RNase protection assay. The RNA:RNA hybrid formed between in vitro transcribed radiolabeled RNA and target RNA is shown (left). Treatment with RNase A/T1 removes single-stranded regions and leaves protected psnoRNAs (right). b Expression of MBII-52 and MBII-85 snoRNAs in HEK293T cells and mouse brain. HEK293 cells were transfected with snoRNAs expression constructs (1 μg plasmid per 1 ml media). Total RNA was isolated from mouse brain (brain) and HEK293 cells (cells) after 42 h of transfection and analyzed by RNase protection assay as described (Shen et al. 2011). Arrows show full-length snoRNAs, additional lower bands show snoRNAs processing products. c RT-qPCR amplification of miRNAs encoded in intron 2. Total RNA was extracted from HEK293 cells transfected with control plasmid-expressing EGFP-C2, MBII-52 or MBII-85 snoRNAs (n = 4). d RT-PCR amplification of the flanking intron 2, and the amplification of β-actin mRNA as loading control. e Quantification of RT-PCR results shown on 4D. Exon 2 and 3 expression normalized to the expression of β-actin and plotted on a chart
