FIGURE 2.
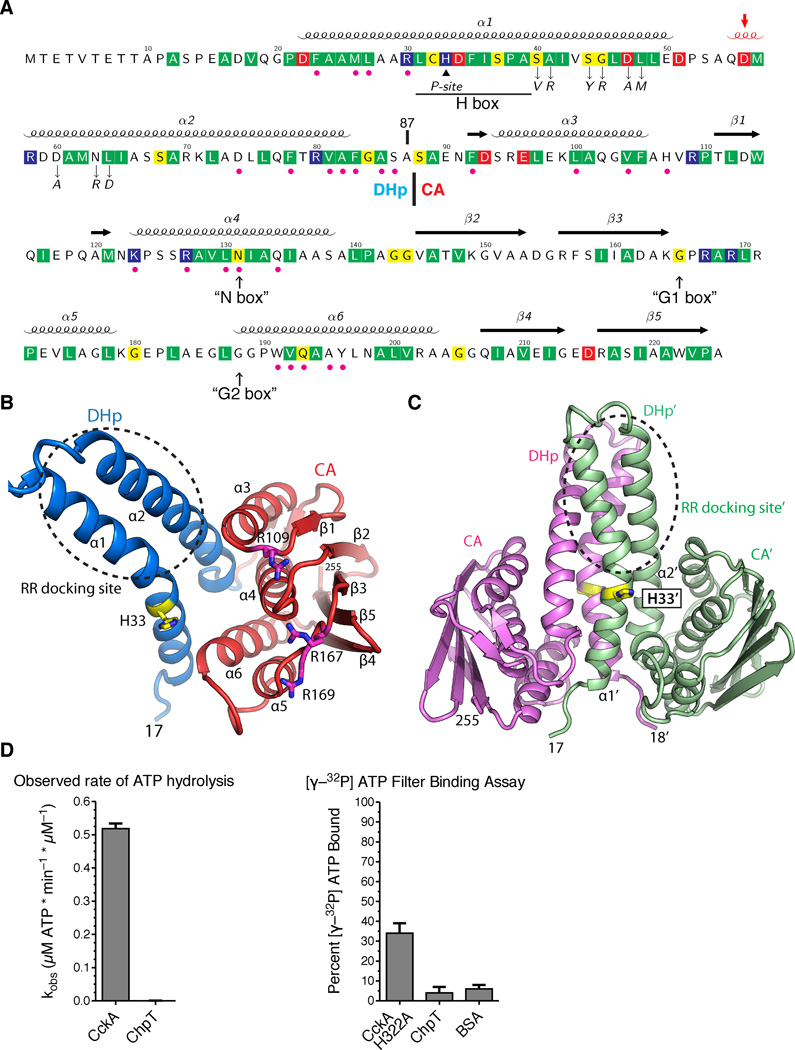
The ChpT crystal structure shows a pseudo-HK fold. A. The annotated ChpT primary sequence with the secondary structure elements shown above (the 310 helix in red and indicated by an arrow). Conserved residues among ChpT orthologs are highlighted in colors (red, acidic; blue, basic; yellow, polar uncharged; and green, hydrophobic nonpolar). Magenta dots denote the residues at the DHp-CA interfaces, and the black triangle denotes the site of phosphorylation (His33). Residues that are subjected to point mutations are denoted by down arrows. The expected locations for degenerate HK sequence motifs are shown at the bottom (in quotes and up arrows). The domain boundary between the DHp and CA domains is located at residue 87. B. The domain organization of a ChpT monomer colored by domain (CA - red, DHp - blue). His33 and conserved arginines on the surface of CA domain are shown as sticks. C. A ChpT homodimer contains a four-helix bundle formed by two DHp domains. One ChpT molecule is colored magenta; the other is colored sea-green. His33, the site of phosphorylation, is shown in sticks. A circle highlights the site for interaction with RRs. D. A coupled-enzyme assay confirms ChpT cannot catalyze ATP hydrolysis. E. An ATP filter binding assay confirms ChpT cannot bind ATP (see also Fig. S1).