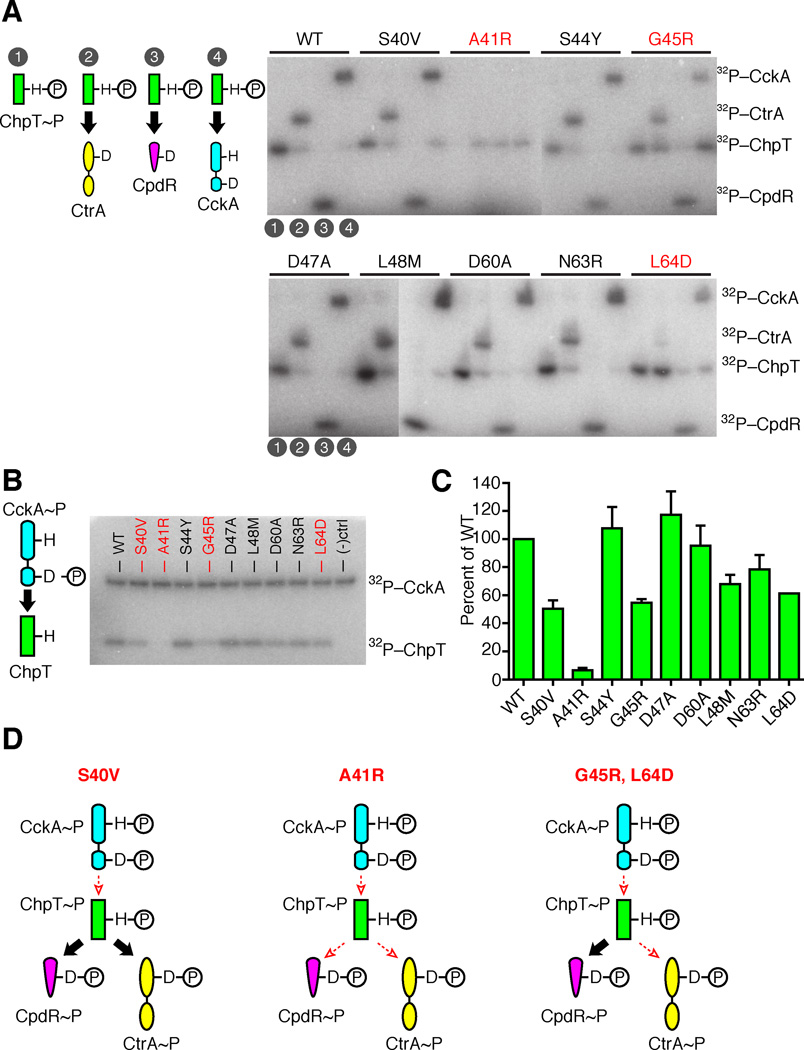
FIGURE 4.
An essential surface on ChpT governs its RR interactions. A. For each ChpT mutant, ChpT~P was generated by incubation with FLAG-CckA, then subsequently purified to remove FLAG-CckA and ATP. Purified ChpT~P mutants were incubated for 10 s with either (1) ChpT~P only, (2) ChpT~P + SUMO-CtrA, (3) ChpT~P + CpdR, (4) ChpT~P + FLAG-CckA. B. A phosphotransfer assay between CckA and ChpT variants with point mutations in the putative RR binding region. CckA~P autophosphorylated in [γ-32P] ATP was mixed with each ChpT variant and allowed to react for 10s before quenching. The phosphoproteins were separated by SDS-PAGE and imaged by phosphor storage. Negative control lane was a reaction mixture lacking ChpT. C. Quantitation of three replicate phosphotransfer assays between CckA~P and ChpT variants with mean intensity and standard deviation of each ChpT~P band shown. D. Classification of ChpT mutants as deficient in CckA-ChpT phosphotransfers, deficient in all phosphotransfers, or deficient in phosphotransfers between CckA-ChpT and ChpT-CtrA. Large black arrows indicate efficient phosphotransfer between signaling partners, whereas small, dashed, red arrows indicate diminished phosphotransfer (see also Fig. S3).