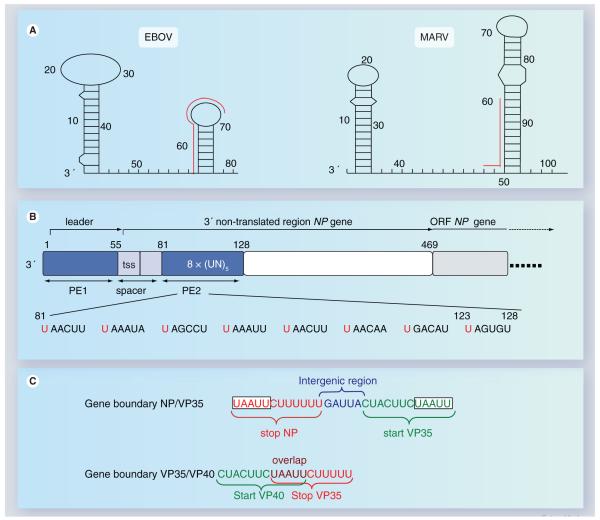
Figure 4. Cis-acting elements on filovirus genomes.
(A) RNA secondary structure formation at the 3′ terminus of MARV and EBOV genomes. The first predicted RNA secondary structure is located within the leader region of each genome, the second RNA stem-loop structure is formed by the respective first transcription start site and downstream-located sequences. The red lines running along the side of the stem-loops identify the transcription start signals. Predicted panhandle structures formed by complementary regions of the 3′ and 5′ ends are not shown. Nucleotide numbers refer to the genomic RNA of Zaire ebolavirus, strain Mayinga (accession number AF086833) and Lake Victoria marburgvirus, strain Musoke (accession number DQ217792), respectively. (B) Structure of the Zaire ebolavirus genomic replication promoter. The promoter is located at the 3′ end of the genome. It is bipartite consisting of PE 1 and 2. PE 1 and 2 are depicted as blue boxes. PE 1 and 2 are separated by a spacer (light blue) that contains the transcription start signal of the NP gene. PE 1 spans the leader region, PE 2 is located within the nontranslated region of the NP gene and consists of a stretch of eight UN5 hexamers. The ORF of the NP gene is depicted in light gray. The nucleotide sequence of PE 2 is shown below the scheme. Conserved hexameric U residues are indicated in red. (C) Two typical gene boundaries within the EBOV genome. Transcription start signals are shown in green, transcription stop signals in red. Intergenic region is shown in blue, gene overlap in purple. A conserved pentamer, which is part of the transcription start signals as well as of the transcription stop signals, is boxed.
EBOV: Ebola virus; MARV: Marburgvirus; NP: Nucleoprotein; ORF: Open-reading frame; PE: Promoter element; tss: Transcription start signal; VP: Viral protein.