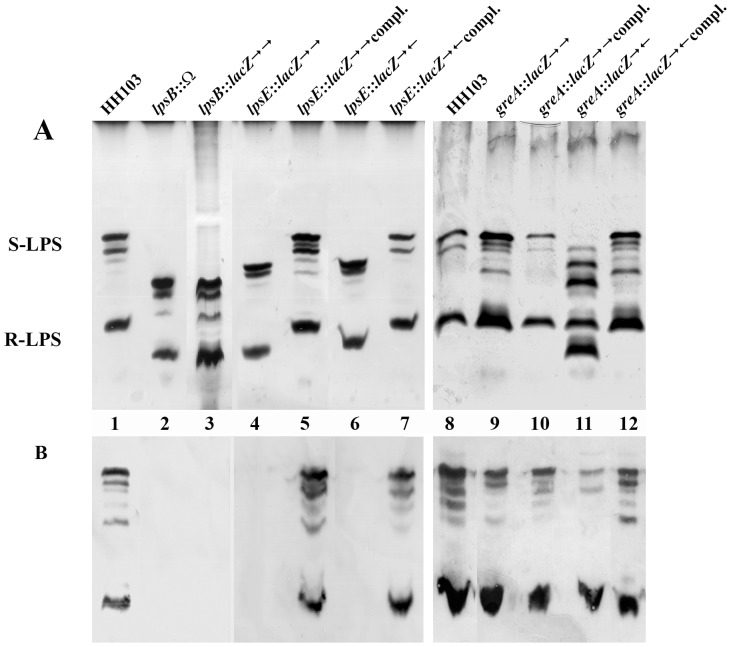
Figure 2. S. fredii HH103 lpsB and lpsE mutants and the greA mutant SVQ656 are affected in LPS production.
A, sodium dodecyl sulphate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and silver-staining or B, immuno-staining using the monoclonal antibody NB6-228.22 of lipopolysaccharides (LPS) crude extracts from Sinorhizobium fredii HH103 and its lpsB (SVQ613, SVQ615), lpsE (SVQ642, SVQ647), and greA (SVQ655, SVQ656) mutant derivatives. Lanes 1 and 8, HH103 RifR; lane 2, SVQ613; lane 3, SVQ615; lane 4, SVQ642; lane 5, SVQ642 C1; lane 6, SVQ647; lane 7, SVQ647 C2; lane 9, SVQ655; lane 10, SVQ655 carrying pMUS908; lane 11, SVQ656; lane 12, SVQ656 carrying pMUS908. The rough and smooth forms of the wild-type LPS are indicated as R-LPS and S-LPS, respectively. The relevant characteristics (gene mutated, cassette employed and, when necessary, orientation of the cassette) are indicated on the top of each lane. Compl. = complemented.