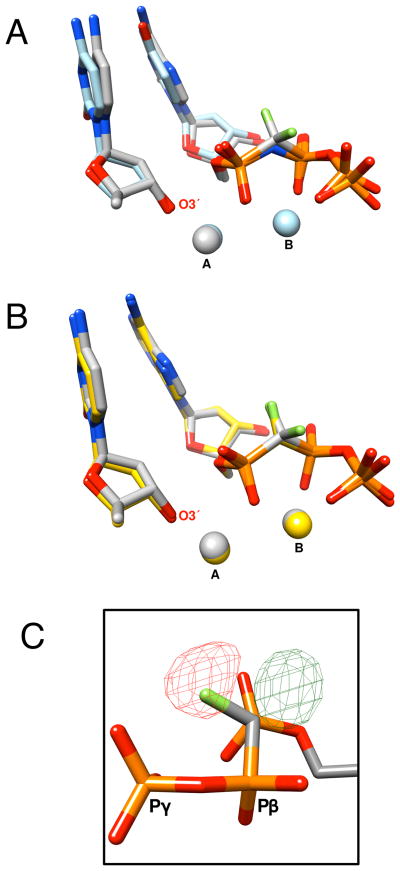
Figure 3.
A) The ternary complex crystallographic structures of pol β with an incoming α,β-CF2-dATP (7) (gray carbons) and α,β-NH-dUTP (light blue carbons; PDB ID 2FMS)[8] were superimposed using all 326 Cα (rmsd = 0.29 Å). The incoming nucleoside triphosphates are shown as well as the primer terminal nucleoside (O3′ is labeled). The position of the active site Mg2+ (spheres) are colored according to the respective carbons. A and B refer to the catalytic and nucleotide binding metal, respectively. B) The ternary complex crystallographic structures of pol β with an incoming 7 (gray carbons) and α,β-CHF-dATP (6b) (yellow carbons) were superimposed using all 326 Cα (rmsd = 0.15 Å). C) A difference density map generated using the R-CHF isomer shows both positive (green, contoured at 3.2σ) and negative density (red, contoured at 4.0σ) in the vicinity of the position of the proposed fluorine atom indicating that the orientation for the R-isomer is not correct.