Figure 1.
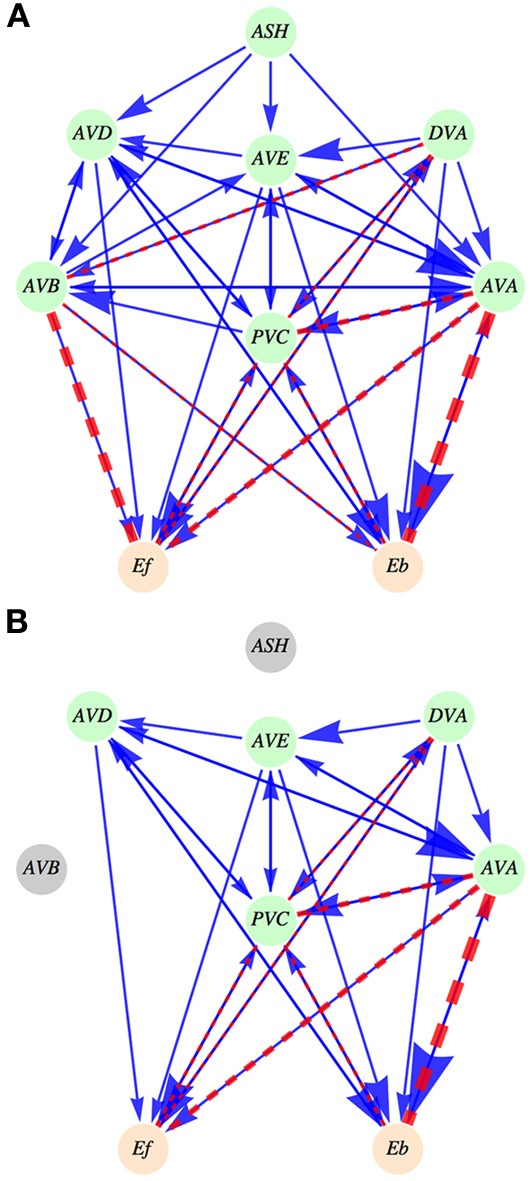
Schematic diagram of the interneuron locomotory circuit. (A) Intact circuit. ASH neuron is an upstream neuron that provides synaptic input to the locomotory interneurons. The output coming from the six neurons (five interneurons and DVA) feeds the activities of motor neurons, represented by Ef (controlling forward motion) and by Eb (controlling backward motion). Synaptic connections are shown as solid arrows (blue), and gap junctions are represented by dashed lines (red). The magnitude of an arrow and the width of a dashed line are indicators of the strength of synaptic and gap junction connections, respectively. (B) An example of an ablated circuit, in which ASH and AVB neurons are removed. Note that this leads to the removal of all connections (synaptic and electric) coming out from these neurons. Such ablations not only change the circuit architecture but also modify its activity output.
