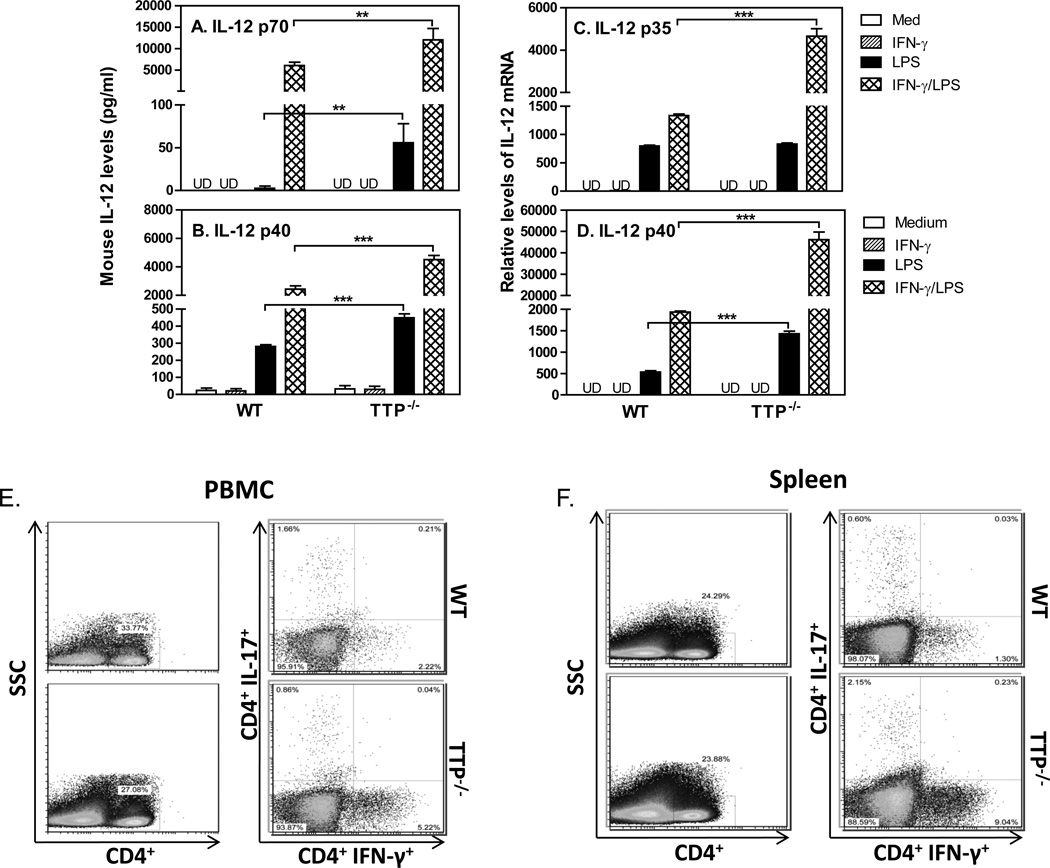
Figure 2. TTP inhibits IL-12 production and Th1 cells.
1 × 106 mouse peritoneal macrophages isolated from WT and TTP−/− mice were incubated in 24-well plate with 1 ml RPMI 1640 complete medium. The cells were stimulated with IFN-γ (10 ng/ml), LPS (1 µg/ml) or IFN-γ plus LPS for 24 hours, followed by collection of supernatant to measure the levels of IL-12 p70 (A) and IL-12 p40 (B) with ELISA, or by RNA extraction to quantify IL-12 p35 (C) and IL-12 p40 (D) mRNA expression with qRT-PCR. qRT-PCR data were normalized relative to GAPDH mRNA expression levels in each sample and further normalized to the results from the untreated group (Medium). Data shown are mean plus SD from three independent experiments. CD4+ T cells were purified by negative selection from PBMCs and spleens of untreated WT and TTP−/− mice. The CD4+ T cells were stimulated with PMA and Ionomycin for 3–4 hours before staining. IFN-γ-producing CD4+ T cell populations were analyzed by FACS in PBMCs (E) and spleens (F) from WT and TTP−/− mice by gating on CD4+ cells. Data represent one of three experiments with similar results.