Figure 1. Tat–beclin 1 peptide induces autophagy in vitro.
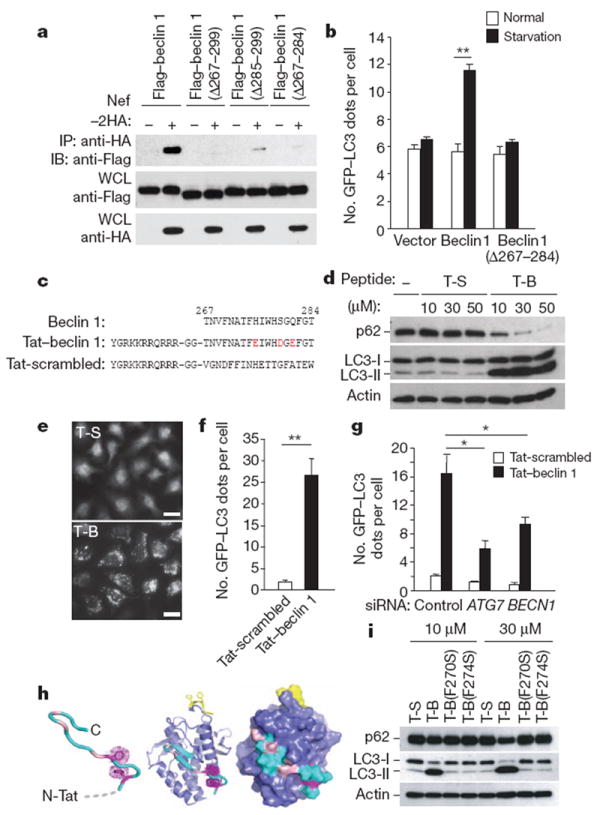
a, Immunoprecipitation of Flag–beclin 1 constructs with Nef–HA in HeLa cells 24 h post-transfection. b, GFP–LC3-positive dots (autophagosomes) in MCF7 cells expressing GFP–LC3 and Flag–beclin 1 constructs grown in either normal medium or starved in EBSS for 2 h. c, Sequences of beclin 1 amino acids 267–284, Tat–beclin 1 (T-B) and Tat-scrambled (T-S) control peptide. Red letters indicate amino acid substitutions to enhance hydrophilicity. d, Biochemical assessment of autophagy (p62 and LC3 immunoblots) in peptide-treated HeLa cells (3 h). e, f, Representative images (e) and quantification of GFP–LC3-positive dots (f) in peptide-treated HeLa/GFP–LC3 cells (30 μM, 3 h). Scale bars, 20 μm. g, GFP–LC3-positive dots in siRNA-transfected peptide-treated HeLa/GFP–LC3 cells (30 μM, 3 h). h, Model of Tat–beclin 1 peptide (left) based on corresponding elements of the beclin 1 evolutionarily conserved domain (ECD) structure (centre). Essential phenylalanine side chains, magenta; positions of solubility mutations, pink; lipid interaction site, yellow. ECD surface representation (right) illustrates exposure of corresponding peptide (cyan). i, p62 and LC3 immunoblots in peptide-treated HeLa cells (3 h). In b, f, g, bars represent mean ± s.e.m. of triplicate samples (50–100 cells per sample). Similar results were observed in three independent experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01; t-test.
