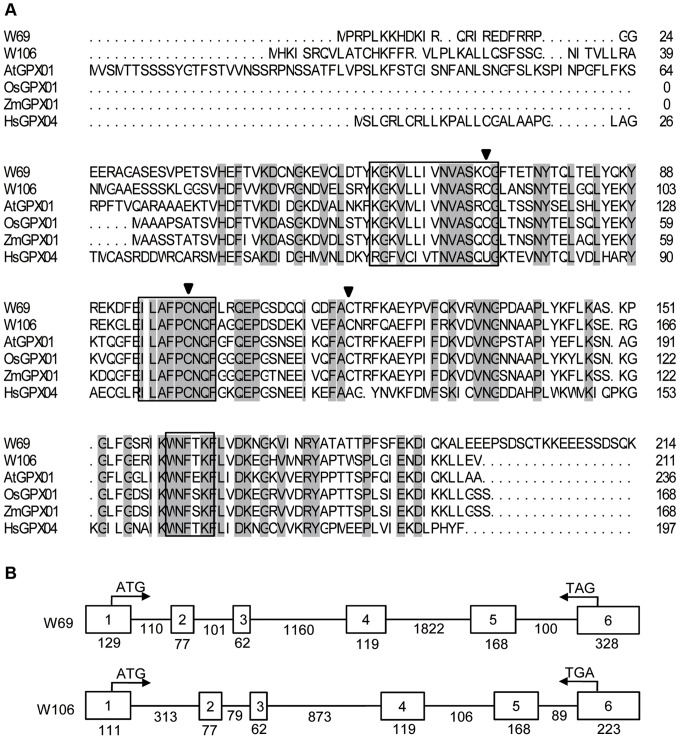
Figure 1. Alignment of W69 and W106 with other GPXs from plants and their exon-intron structures.
(A) Alignment of GPX protein sequences with other species: Oryza sativa (OsGPX01, accession number: NC008397), Zea mays (ZmGPX01, AY542310) and Homo sapiens (HsGPX04, P36969). Gray background represents strictly conserved amino acids. Boxed sequences represent highly conserved domains (G1,G2,and G3). The SeCys residues of the mammalian PHGPXs (HsGPX04) are denoted by “U”, the three conserved Cys of these isoenzymes are marked by inverted triangles. (B) Exon-intron structure of the GPX homologs. The chromosomal structures of the GPXs were constructed by comparing mRNA sequences with their respective genomic sequences. The length of each exon (square) and intron (line) is given. The W69 gene starts with ATG at position 75 bp in exon 1 and ends with TAG at position 81 bp in exon 6; the W106 gene starts with ATG at position 56 bp in exon 1 and ends by TGA at position 29 bp in exon 6.