Figure 1.
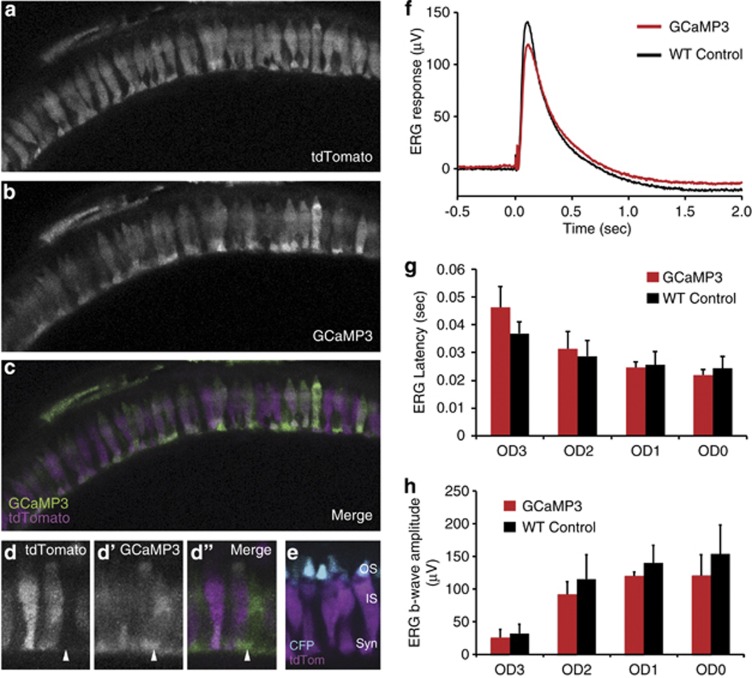
GCaMP3 is expressed in all cone photoreceptors and does not interfere with light responses. (a–c) Retinal slice projections from a representative 5 d.p.f. Tg(Trß2:tdTomato;TαCP:GCaMP3) double-transgenic pde6cw59 mutant zebrafish larvae displaying intact photoreceptors prior to their degeneration. The tdTomato (a) is expressed only in long-wavelength cones, whereas the GCaMP3 (b) is expressed in all cone photoreceptors. Panel c shows both tdTomato (magenta) and GCaMP3 (green) channels merged. (d) Magnified view of cone photoreceptors in the Tg(Trß2:tdTomato;TαCP:GCaMP3) double transgenic. Arrow indicates a cell expressing GCaMP3 (green) but not tdTomato (magenta). Less expression of both GCaMP3 and tdTomato is observed in the cone outer segments (OS), whose location within the photoreceptor layer is clearly defined by the TαCP:membrane CFP (membrane cyan fluorescent protein (mCFP); cyan) transgene (e) Retinal section from a Tg(Trß2:tdTomato; TαCP:mCFP) double-transgenic fish expressing tdTomato in long-wavelength cones (magenta) and membrane CFP (cyan) in all cones. The outer segments (OS), inner segments (IS), and synapses (syn) are as indicated. (f–h) ERG waveforms (f), b-wave latencies (g), and b-wave amplitudes (h) for 5 d.p.f. WT non-transgenic versus Tg(TαCP:GCaMP3) larvae show no significant differences in their light responses over three orders of magnitude. n=3 fish per condition; bars=S.D.