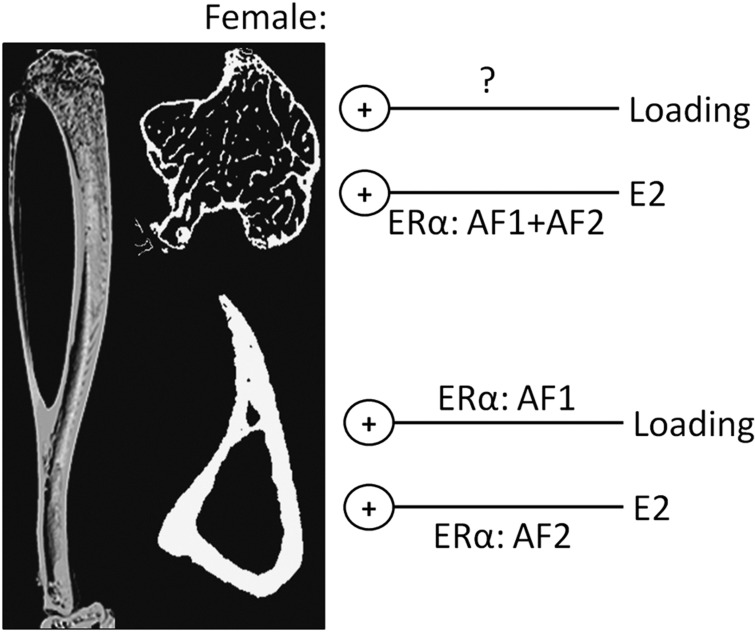
Figure 3.
The osteogenic effects of loading and estrogen (E2) on trabecular and cortical bone of female mice are differentially mediated by its activation function 1 (AF1) and AF2 domains. Deletion of either the AF1 or AF2 domains of estrogen receptor α (ERα), or complete ERα deletion, does not impair the osteogenic response of loading on female trabecular bone, whereas deletion of either domain reduces trabecular bone gain following treatment with estrogen. In cortical bone, deletion of the AF1 domain impaired the osteogenic response to loading, whereas only deletion of the AF2 domain impaired the increase in cortical bone mass following treatment with estrogen.