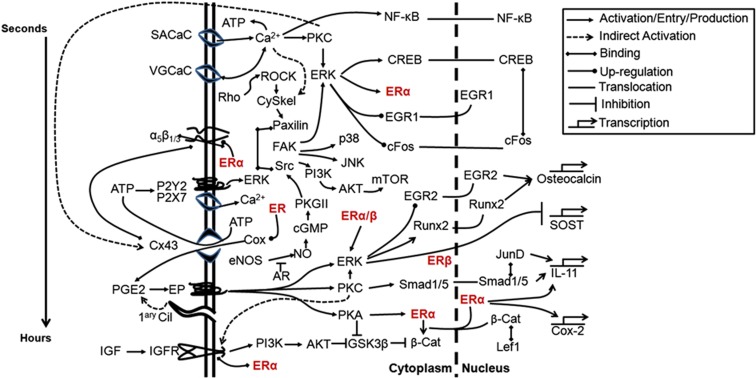
Figure 4.
Schematic representation of the involvement of estrogen receptor (ER) in signaling pathways activated by mechanical stimulation of osteoblastic cells. Membrane-initiated signaling events are grouped temporally from stretch-activated calcium channels (SACaC) activated within seconds, to voltage-gated calcium channels (VGCaC), integrins including α5β1/3, ATP's P2 receptors, connexion (Cx)43 hemichannels, PGE2's EP receptors, the primary cilium (1ary Cil) and the insulin-like growth factor (IGF) receptor. The ERs (red) are emphasized to illustrate their contribution to several pathways. Timing of intracellular signaling is difficult to dissect because of cross-talk between different pathways but a general timeframe is indicated (left). AKT, protein kinase B; AR, androgen receptor; cGMP, cyclic guanosine monophosphate; CREB, cAMP response element binding protein; eNOS, endothelial nitric oxide synthase; EP, E series prostaglandin receptors; FAK, focal adhesion kinase; GSK3β, glycogen synthase kinase 3β; IL, interleukin; JNK, c-Jun N-terminus kinase; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; NF-κB, nuclear factor κB; PGE2, prostaglandin E2; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinase; PKC, protein kinase C.