Figure 8. The hepatic Gck mRNA (A) and GK enzyme activity (B) in livers of Zucker lean rats fed with VAS and VAD diets and the Gck mRNA in livers of Sprague–Dawley rats in steady state (C) and after treatment of VAD rats with RA administered intraperitoneally (D).
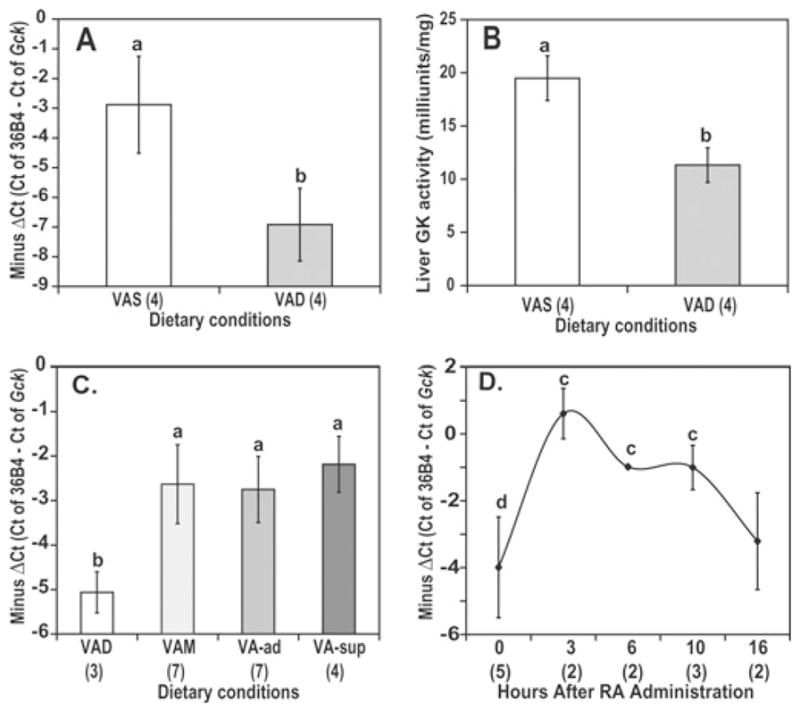
(A, B) Zucker lean rats were fed with VAD and VAS diet for 9 weeks. (C) Different categories of VA status were produced by feeding rats with one of four diets: VAD, VAM, VA-Ad and VA-Sup. (D) VAD rats received a single intraperitoneal administration of 100 μg of RA. Individual VAD rat livers were collected for analysis at the indicated time points. The results are presented as − ΔCt [−ΔCt = (Ct of 36B4) − (Ct of Gck )] for mRNA and m-units/mg of GK enzyme activity. Total RNA was isolated from individual rat livers (a > b; c > e, f; and d > f, all P < 0.02). Animal number, n, per group is shown in parentheses.
