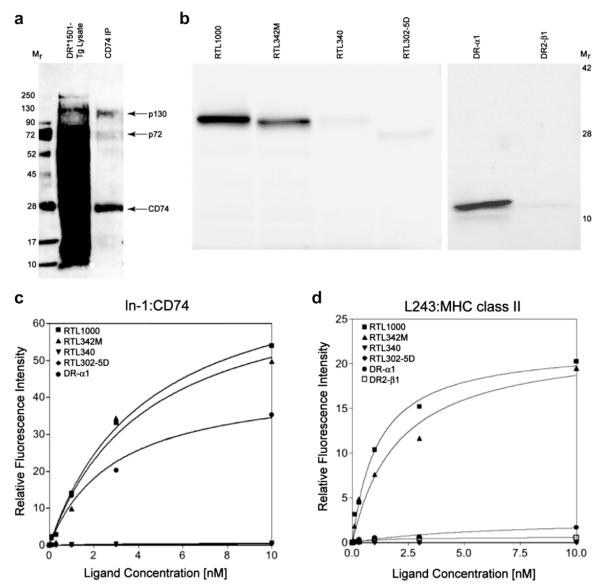
Fig. 3.
Binding of RTL constructs to immunopurified membrane CD74 and MHC class II. a) The lysate from membrane-biotinylated splenocytes from DR*1501-Tg mice was mixed with ln-1 bound to Protein L beads overnight at 4 °C. Immune complexes were washed 3 times with 1% CHAPS in TEN buffer (50 mM TRIS, 2 mM EDTA and 150 mM NaCl, pH 7.4) and once with TEN buffer to remove free material. Bound proteins were eluted by boiling the immune complexes in electrophoresis sample buffer for 8e10 min followed by centrifugation. Samples were analyzed by SDS-PAGE followed by Western blot and proteins were visualized using streptavidin-conjugated PE. The membrane was scanned in a Molecular Imager FX (BioRad) for PE fluorescence. M: molecular weight markers; DR*1501-Tg Lys: total lysate; CD74 IP: immunoprecipitated CD74. b) To evaluate binding of other RTL constructs, CD74 protein complexes were immunoprecipitated from biotin-labeled DR*1501-Tg splenocytes using ln-1 adsorbed onto Protein L/beads and incubated overnight with 250 nmols of FITC-labeled RTL, FITC-DR-α1 or FITC-DR2-β1 domains. Beads were washed 3 times and bound fluorescent RTL components were eluted as described above and analyzed by SDS-electrophoresis in a 10–20% PAGE. Gels were directly scanned for FITC chromophore as mentioned for panel a) and band intensity was determined by densitometry in a Molecular Imager FX (BioRad) with the Quantity One Software. c) FITC-labeled-RTL1000 (DR2/hMOG-35-55), RTL342M (DR2/mMOG-35-55), RTL340 (DR2/MBP-85-99) and the DR-α1 domain binding to ln-1 immunoprecipitated CD74 or d) L243-immunoprecipitated MHC class II was analyzed as a function of their concentration. Band intensity was determined by densitometry as described above. To isolate MHC class II, lysates were first depleted of CD74 with ln-1 bound to Protein L/beads overnight at 4 °C and the supernatant was subjected to a second round of immunoprecipitation with anti-human class II L243 monoclonal antibody adsorbed to Protein L/beads. Data from densitometry were plotted as ligand concentration vs. fluorescence intensity and analyzed using the Prism Software for one- or two-site binding with R2 > 0.95 for all bound RTL. Binding constants (KD) of RTL constructs to CD74 and MHC class II assessed in this experiment are presented in Supplementary Fig. 5. All FITC-labeled bands were detected in a Bio-Rad Imager FX scanner followed by quantification by densitometry using Quantity One Software. Data were normalized and plotted vs. the RTL concentration and the curve was fit to one-site or two-site competition models and binding constants determined using the Prism Software. The best fit was found with the one-site competition equation.