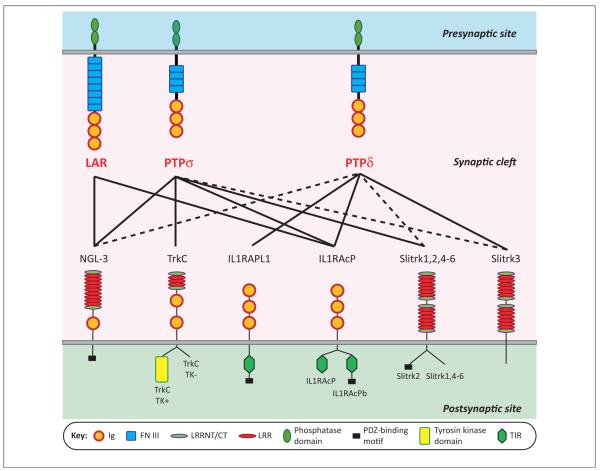
Figure 2.
The selective binding code of receptor-type protein tyrosine phosphatases (RPTPs) with diverse postsynaptic partners. Individual RPTPs bind to overlapping sets of postsynaptic partners, as indicated by the lines; broken lines indicate interactions that can occur in vitro but appear to lack physiological relevance. Importantly, except for netrin-G ligand-3 (NGL-3), these interactions are regulated by alternative splicing of RPTPs at the meA and meB sites. Neurotrophin receptor TrkC can bind all PTPσ forms but insertions at the meA and meB splice sites reduce the apparent interaction [7]. Interleukin-1 receptor accessory protein (IL1RAcP) can bind all forms of PTPδ but insertions at the meA and meB splice sites enhance this interaction [10]. Interleukin-1-receptor accessory protein-like 1 (IL1RAPL1) shows a more complicated selectivity code, binding best to PTPδA9+B+ and PTPδA6+B+, the two most prevalent forms detected in postnatal day 11 (P11) mouse brain, as well as PTPδA9+B− (+ indicates the presence of an insert and the number indicates the length) [8].