Figure 4.
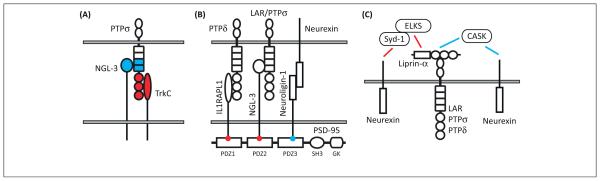
Cooperative mechanisms among receptor-type protein tyrosine phosphatase (RPTP)-based and neurexin-based synapse organizing complexes. (A) Netrin-G ligand-3 (NGL-3) and the neurotrophin receptor TrkC bind to distinct domains of PTPσ [the first two fibronectin III (FNIII) domains for NGL-3 [6] and the Ig domains for TrkC [7]]. Therefore, NGL-3 and TrkC could cooperatively regulate excitatory synapse organization through possible simultaneous binding to PTPσ. Although domain mapping has not been reported for the other RPTP partners, their regulation by meA and meB splicing suggests that interleukin-1-receptor accessory protein-like 1 (IL1RAPL1) and interleukin-1 receptor accessory protein (IL1RAcP) also bind to the Ig domains. Thus, NGL-3, which can bind to all RPTPs, might be rather unique in simultaneously binding to RPTPs along with a variety of other postsynaptic partners. (B) NGL-3 and IL1RAPL1 can each bind to the first two PDZ domains of PSD-95 [50,62], and neuroligins bind to the third PDZ domain of PSD-95 ([127]). Leucine-rich repeat transmembrane proteins (LRRTMs) also bind PSD-95 [69], Thus, scaffolding by PSD-95, which itself forms head-to-head multimers, and other members of the MAGUK family, may stabilize many of these trans-synaptic complexes and function to transduce the anterograde synapse organizing signal by recruiting postsynaptic receptors, other scaffolds, and signaling proteins. (C) The most direct known link from RPTPs to neurexins is through liprin-α binding to CASK, which in turn binds to neurexins [128]. However, cultured cortical neurons lacking CASK exhibit normal evoked glutamatergic and GABAergic transmission [129] and Caenorhabditis elegans liprin-α and CASK orthologs Syd-2 and Lin-2 do not colocalize or genetically interact [39], raising questions about the importance of this link. Another key pathway recently identified in Drosophila [130] links the neurexin DNrx-1 to the liprin-α DSyd-2 through DSyd-1, a Rho GTPase-activating protein that contains PDZ and C2 domains initially identified from a C. elegans screen for genes contributing to synapse development [131]. It is not yet clear whether Syd-1 directly binds liprin-α or whether they interact through simultaneous binding to ERC [132].
