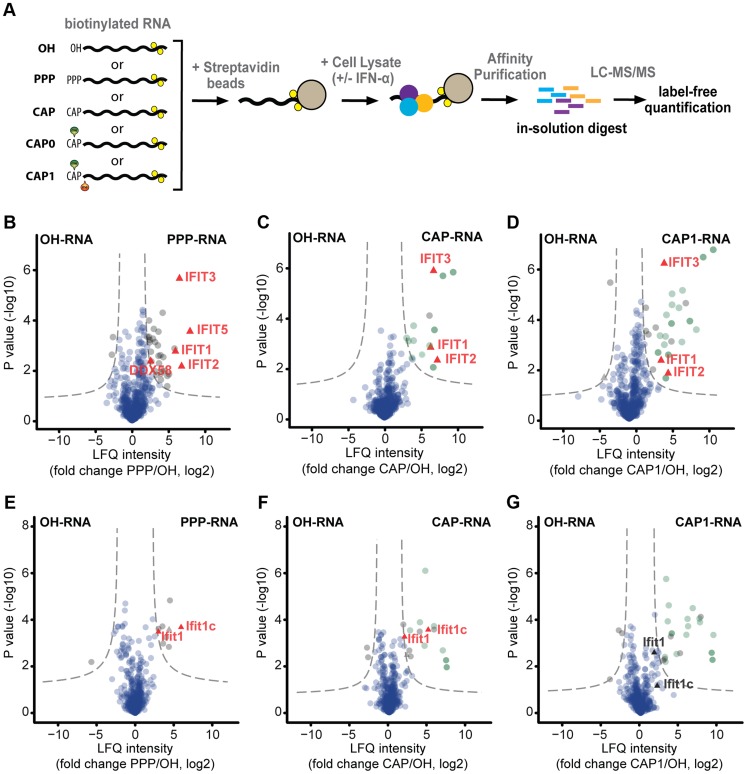
Figure 1. Mass spectrometry-based identification of human and murine interactors of capped RNA.
(a) Schematic depiction of the experimental approach used for mass spectrometry (MS)-based identification of cellular RNA binding proteins. Biotinylated RNA with different 5′ end structures (OH, PPP, CAP, CAP0, CAP1) was coupled to streptavidin beads, and incubated with lysates obtained from cells that had been left untreated or treated with 1000 U/ml IFN-α for 16 h. Bound proteins were denatured, alkylated and directly digested with trypsin. The resulting peptides were subjected to shotgun liquid chromatography-tandem MS (LC-MS/MS). Three independent experiments were performed for each RNA bait, and the data were analysed with the MaxQuant software [37] using the label-free quantification algorithm [38]. (b–d) Proteins obtained from lysates of IFN-α-treated HeLa cells using the indicated biotinylated RNA baits were analysed by LC-MS/MS. Volcano plots show the degrees of enrichment (ratio of label-free quantitation (LFQ) protein intensities; x-axis) and p-values (t-test; y-axis) by PPP-RNA (b), CAP-RNA (c), and CAP1-RNA (d) baits as compared to OH-RNA. Significantly enriched interactors (see Materials and Methods) are separated by a hyperbolic curve (dotted line) from background proteins (blue dots), known cap-binding proteins (dark-green), and proteins known to associate with capped RNA (light green). Interferon-induced proteins [21] detected in the significantly enriched fractions (IFIT1-3 and 5, DDX58) are highlighted (red triangles). (e–g) As in (b–d) but for lysates of IFN-α-treated mouse embryo fibroblasts (MEFs). The interferon-induced proteins Ifit1 and Ifit1c [42] in significantly enriched and non-enriched fractions are highlighted.