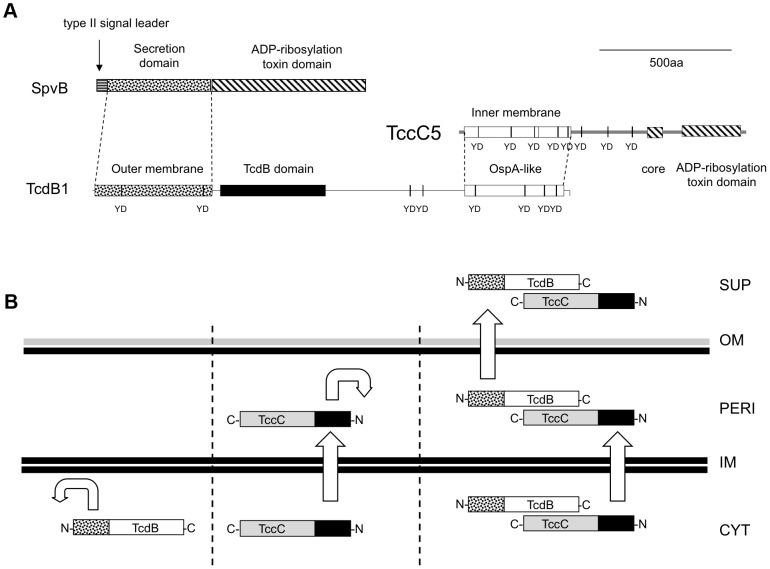
Figure 9. The predicted domain structure and function of B and C-subunits.
(A) Comparisons of domain predictions of B+C sub-complex proteins and the Salmonella SpvB protein. Note, neither the B nor C -subunits contain a predicted type II signal leader present in SpvB. Note the “core” domain represents a highly conserved sequence common to all Rhs/TccC family proteins located adjacent to the variable C-terminal regions. The predicted OspA-like structural domains of the B and C proteins are shown in addition to YD-repeat sequences common to these protein families. The labels “inner membrane” and “outer membrane” on the N-terminal domains of the C and B -subunits reflect their secretion roles. (B) A diagrammatic summary of the fates of B and C-subunit proteins when produced either independently or together. Cellular compartments shown include supernatant (SUP), outer membrane (OM), periplasm (PERI), inner membrane (IM) and cytoplasm (CYT). The C and N-termini of the TcdB and TccC proteins are indicated. The straight and curved arrows show the ability (or not) of N-terminal domains to facilitate aspects of the export process.