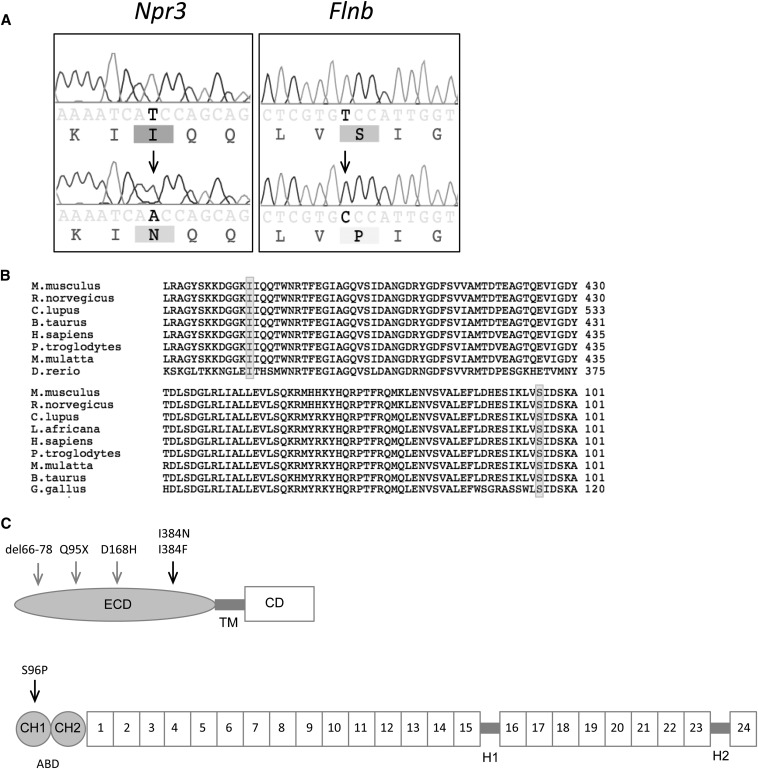
Figure 3.
Identification of mutations underlying skeletal morphology mutant 1 (Skm1) and skeletal morphology mutant 2 (Skm2). (A) Genomic DNA sequence chromatograms from normal (upper) and mutant (lower) Skm1 and Skm2 mice (left panel and right panel, respectively). The location of the mutation is indicated by the arrowhead. (B) Alignment of the amino acid sequence for NPR3 (top) and FLNB (bottom) orthologs. The location of the mutation is indicated by shading. (C) Schematic representation of NPR3 (top) and FLNB (bottom).The arrows indicate location of Skm mutations (black) and other reported mutations (gray). NPR3 contains an extracellular domain (ECD), transmembrane (TM) domain, and cytoplasmic domain (CD). FLNB comprises an actin-binding domain (ABD) containing two calponin homology (CH) domains at the amino terminus, followed by 24 filamin repeat domains that are separated by two hinge (1H-2) regions.